The modern term "alternative" is borrowed from the Latin language ( alternatus– other) for the need to select from several possibilities or to indicate each of these considered possibilities.
Energy sources for heating
The traditional way
Traditional methods of heating an apartment or a private house require the arrangement of a heating system, which includes:
- a heat source that converts the energy of fuel combustion or the energy of network electricity into thermal energy;
- a heat exchanger for transferring thermal energy from an energy carrier to a heat carrier, for the subsequent distribution of heat to heat consumption points;
- a closed pipeline circuit, through which the movement of the coolant is stimulated in a natural or forced way;
- heating devices that distribute heat from the coolant to the environment of the room.
The figure below shows the structure of a heating system with a boiler as a heat source and heat consumption points in the form of radiators and underfloor heating.
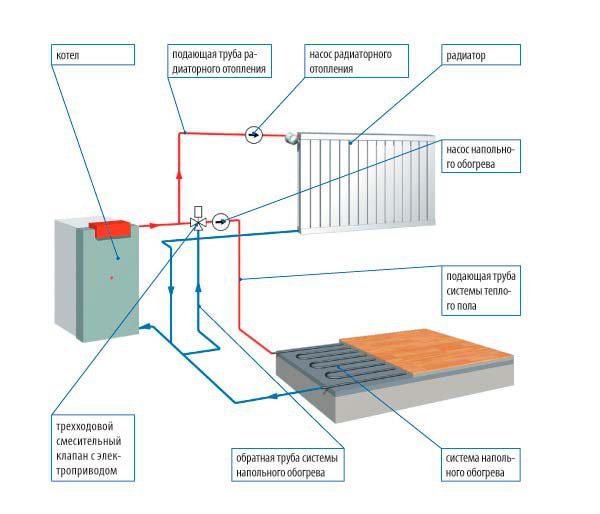 The structure of the traditional heating system of a private house
The structure of the traditional heating system of a private house disadvantages
For most types of heating systems, heating boilers are sources of thermal energy. In them, gas, liquid or solid fuels are burned in order to use the heat of combustion of the fuel to heat the coolant (the so-called gas, liquid fuel and solid fuel boilers).
Another option for heating the coolant in the heat exchanger of the heating boiler is to use the energy of mains electricity (electric heating boilers).
Each type of boiler and the corresponding energy carrier has certain negative features that affect the efficiency of its use:
- Gas-fired boilers are widespread due to the availability of gas.
The negative factors accompanying the use of gas for heating are:
- organizational and technical complexity of connecting to the gas pipeline;
- the threat of ignition or explosion in case of violation of the rules for the operation of gas heating equipment or improper installation by one's own hands;
- rising prices for gas resources.
- Electric boilers are the easiest to install and maintain with your own hands. The most significant disadvantages are:
- volatility of equipment - when the power supply is turned off, the flow of heat into the heating system stops;
- high electricity tariffs.
- Liquid fuel boilers as sources of thermal energy are quite difficult to operate. From the negative, we note the following factors:
- the high cost of liquid fuel, the complexity of its delivery and safe storage;
- noise at work
- unpleasant odors when burning fuel.
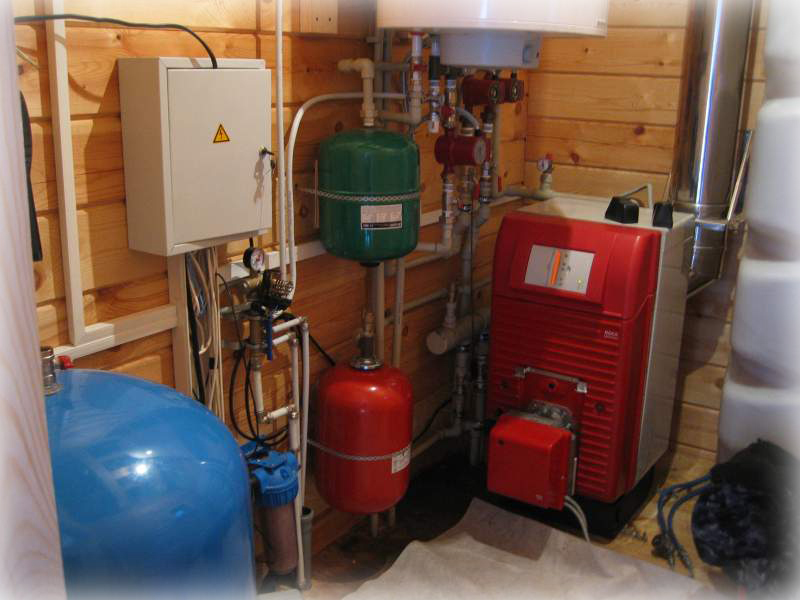 Home boiler room with oil boiler
Home boiler room with oil boiler - Solid fuel boilers on coal, peat, wood or pellets impress with the cheapness of fuel resources and energy independence in operation, but they have their drawbacks:
- fuel loaded with your own hands into the boiler furnace quickly burns out;
- lack of automation of the fuel loading process;
- the need for constant visual monitoring of the operation of the boiler.
All of the above heating systems have two common drawbacks:
- they operate on non-renewable sources of thermal energy - the fuel is completely burned without the possibility of any recovery;
- the operation of equipment that burns natural resources or uses centrally supplied electricity is accompanied by a constant payment for the volume of energy spent and service providers for its provision.
The figure below shows the delivery of liquefied gas for gas heating at home.
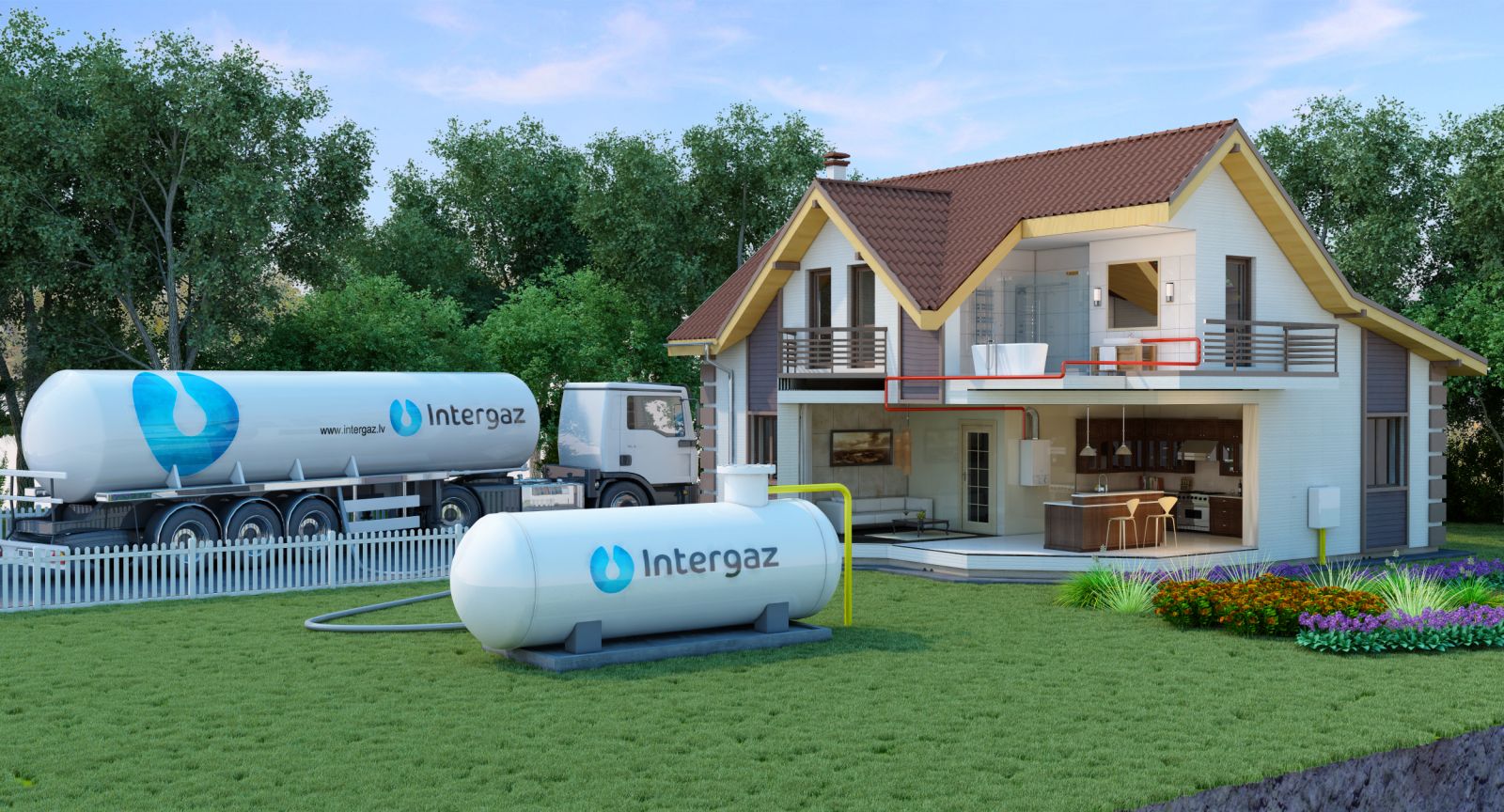 Delivery of liquefied gas to a private house
Delivery of liquefied gas to a private house Nuances that need attention:
- Such a convenient and familiar heating of a private house by burning non-renewable organic resources leads to a catastrophic decrease in natural fuel reserves for money from our own pocket! Naturally, the prices for fossil fuels will constantly rise.
- Combustion of fuel is accompanied by emissions of carbon dioxide and volatile toxic combustion products, and tar and soot fall out.
- Each consumer of organic fuel is forced to equip additional premises:
- for fuel storage;
- for its combustion with the release of combustion products into the atmosphere.
Alternative heating concept
When considering alternative home heating options, you need to decide on the concept itself.
Alternative heat sources for a private house include two fundamentally different types of equipment:
- Devices that work in addition to a self-installed electric or gas boiler. For some reason, a boiler running on gas or electricity does not provide full heat for the heating system of the entire building.
The main heating power is provided by the boiler, and during the period of peak loads or off-season, alternative sources support its operation. In this case, alternative heating will be, for example, a do-it-yourself pellet boiler, or a waste-burning unit, and even infrared heaters.
- Devices that completely replace the boiler on gas, electricity or other traditional energy source. Their heat output is sufficient to provide alternative heating for the home.
The most common alternatives for heating housing without burning gas and other fossil fuels are technologies that use the energy of natural resources - heat from the bowels of the earth, geysers, sunlight and climatic processes - wind, ocean tide.
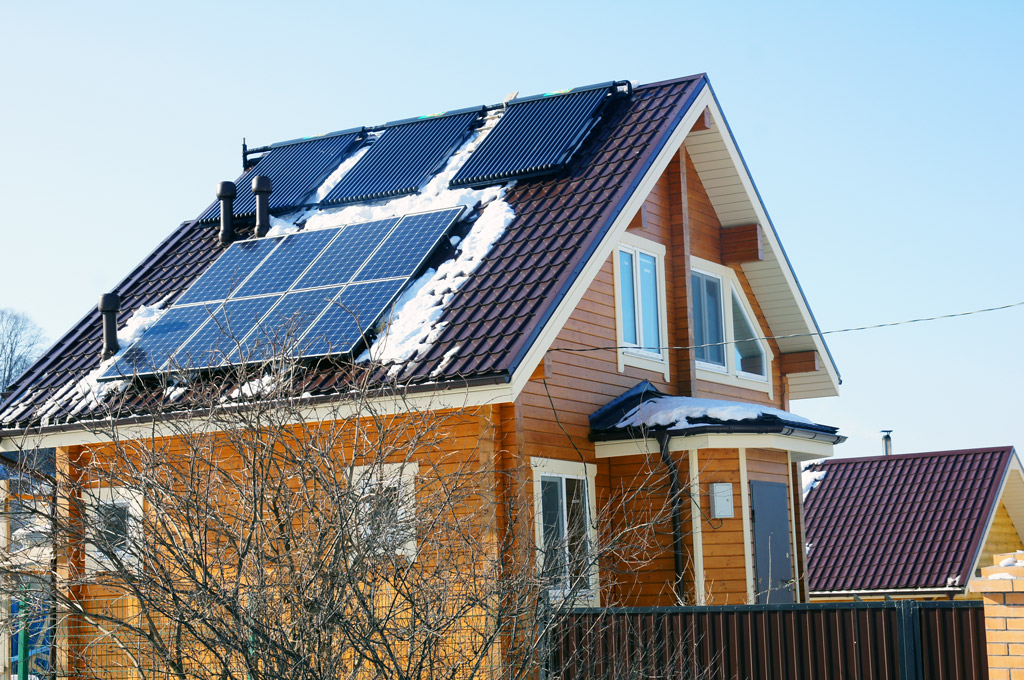 House equipped with solar panels
House equipped with solar panels Modern methods of heating
The practical implementation of projects on the use of the energy of natural resources and phenomena as an alternative source of heat for heating a home most widely affects:
- energy of sunlight (solar thermal systems);
- wind energy (wind energy);
- energy of warm earth interiors (geothermal pumps).
Two options for the practical application of natural energy for the needs of alternative heating of a private house are noted:
- transformation of the energy of a natural phenomenon into electrical energy, which will then be used for autonomous heating, that is, heating the house from its own internal source of electricity;
- direct heating of the working coolant of the heating system.
Solar system
When arranging solar heating systems with their own hands, both options for solar radiation are used:
- Converting sunlight energy into electrical energy using solar panels.
It is customary to call solar batteries a group of semiconductor photoelectronic converters combined in one common module to generate electricity. Several solar modules create a circuit to provide a private house with a certain amount of electricity.
The power of each solar module can be from 50 to 300 watts. The figure below shows the principle of using solar panels for alternative autonomous heating of a building.
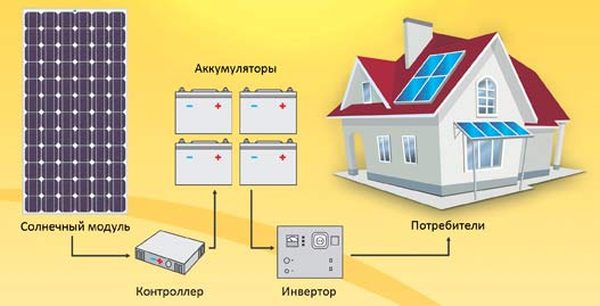 Scheme of heating a house using solar panels
Scheme of heating a house using solar panels The principle of operation of the solar system:
- from the solar module, the converted luminous flux enters the battery pack;
- batteries generate direct current, which is sent to the inverter;
- in the inverter, the direct current is converted into alternating current, which is used to heat the heating elements in the heating system.
Solar panels can only generate electricity. They do not create thermal energy, do not transform and do not accumulate. They work equally effectively on a frosty day or at a positive ambient temperature, since the intensity of the incident solar flux is important to them.
- Use of solar collectors for direct water heating.
In private housing construction, do-it-yourself installation of solar collectors for alternative heating is more popular than installation of solar panels. Collectors convert solar light fluxes directly into thermal energy, bypassing the formation of electricity.
Do-it-yourself collectors for heating have a wide variety of designs, which can be divided into two types:
- flat-plate collectors, consisting of absorbers - elements that absorb sunlight (in the simplest case - metal plates or black sheets) connected to a piping system;
- pipe collectors assembled from glass tubes, inside of which a steel absorber is inserted.
The figure below shows one of the do-it-yourself solar collector options with copper tubes placed in the absorber for heating the coolant.
A coolant with a minimum crystallization threshold is pumped into the tubes. In central Russia, a 60% aqueous solution of propylene glycol with a crystallization onset temperature of -39 0 C is recommended for use.
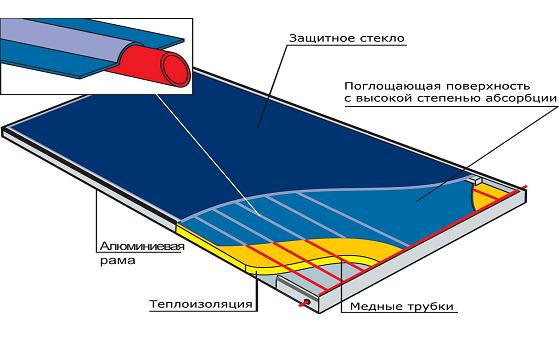 Copper tube solar collector
Copper tube solar collector Both types of collector systems are mounted on the sloping part of the roof of the house. The figure below shows the principle of heating a building using a collector.
The coolant heated in the solar collector (red line) enters the buffer tank, which acts as a heat accumulator and an automated system for maintaining the temperature in the heating and hot water circuits.
If there is a lack of incoming heat on cloudy days, the water in the buffer tank is heated by another available heat source, for example, water from a gas boiler, which is the main heat source of the heating system.
Thanks to automation, the temperature in the heating system is constantly monitored. At night, the lack of solar heat is compensated by connecting a heating element to maintain a comfortable temperature level.
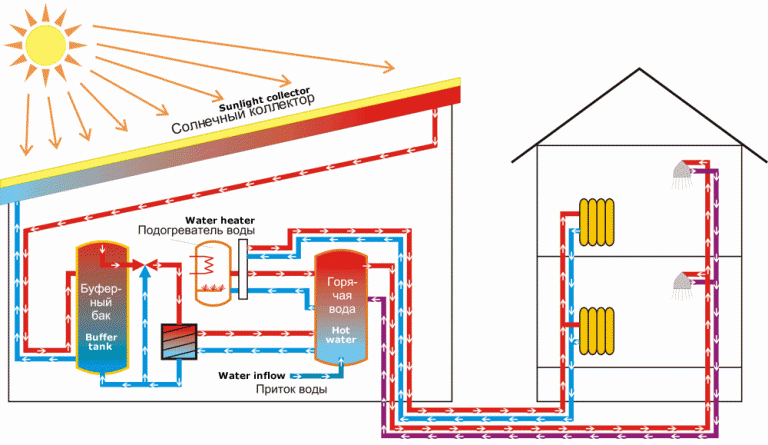 The principle of operation of the heating system from the solar collector
The principle of operation of the heating system from the solar collector home wind power
The use of the kinetic energy of air flows for the needs of heating a private house is carried out in two directions:
- Converting the kinetic energy of the wind into electrical energy by rotating the rotor of special wind generators.
The resulting electricity is stored in batteries and, as needed, through inverters (similar to solar heating technology) is used to heat water in the heating system. In calm weather, heating devices are connected to the general electrical network.
- Converting the energy of the rotating rotor of a wind turbine into thermal energy for direct heating of the coolant using VTG vortex heat generators.
The dominant method in private housing construction is the manufacture and installation of devices consisting of a windmill, a generator and a battery to generate their own electricity. The design captivates with its simplicity and the possibility of self-assembly.
Wind generators differ from each other according to the following indicators:
- the location of the axis of rotation - vertical or horizontal;
- number of propeller blades;
- screw pitch.
The figure below shows a house equipped with wind turbines with a horizontal axis of rotation.
 Wind turbines for power supply of a private house
Wind turbines for power supply of a private house Geothermal (heat) pumps
Devices that can use the geothermal energy of the earth's interior allow owners of private houses to significantly save on gas or other types of fuel when heating their homes. Thermal energy is extracted directly from the depths of the earth or from the bottom of a reservoir using a device called a heat pump.
The principle of operation of a heat pump is similar to the operation of a refrigeration unit using freon:
- when liquid freon passes through pipes at a considerable depth in a reservoir or in a drilled well, in which a positive temperature is maintained even in winter, freon begins to evaporate, turning into a gaseous state;
- the gaseous phase of freon rises up and enters the compressor, which compresses it strongly;
- when gas is compressed in a limited volume, it is heated up to 80 degrees C;
- freon is cooled in the heat exchanger;
- in the throttle chamber, due to a decrease in temperature and pressure, freon again turns into a liquid;
- the cycle is repeated.
Heat pumps are energy-dependent units, however, the power consumption for the operation of the device is disproportionately lower than would be required for direct electrical heating of the coolant.
The temperature of the coolant in the heating system with geothermal devices does not exceed 50 degrees, which is not enough for radiator heating, but for “warm floors” it is quite enough.
Heat pumps structurally differ in the technology of heating freon until it passes into a gaseous state. Depending on the source of "low-level heat" emit:
- water installations for obtaining heat from surface reservoirs or underground groundwater;
- earthen, "taking away" heat from the ground;
- air.
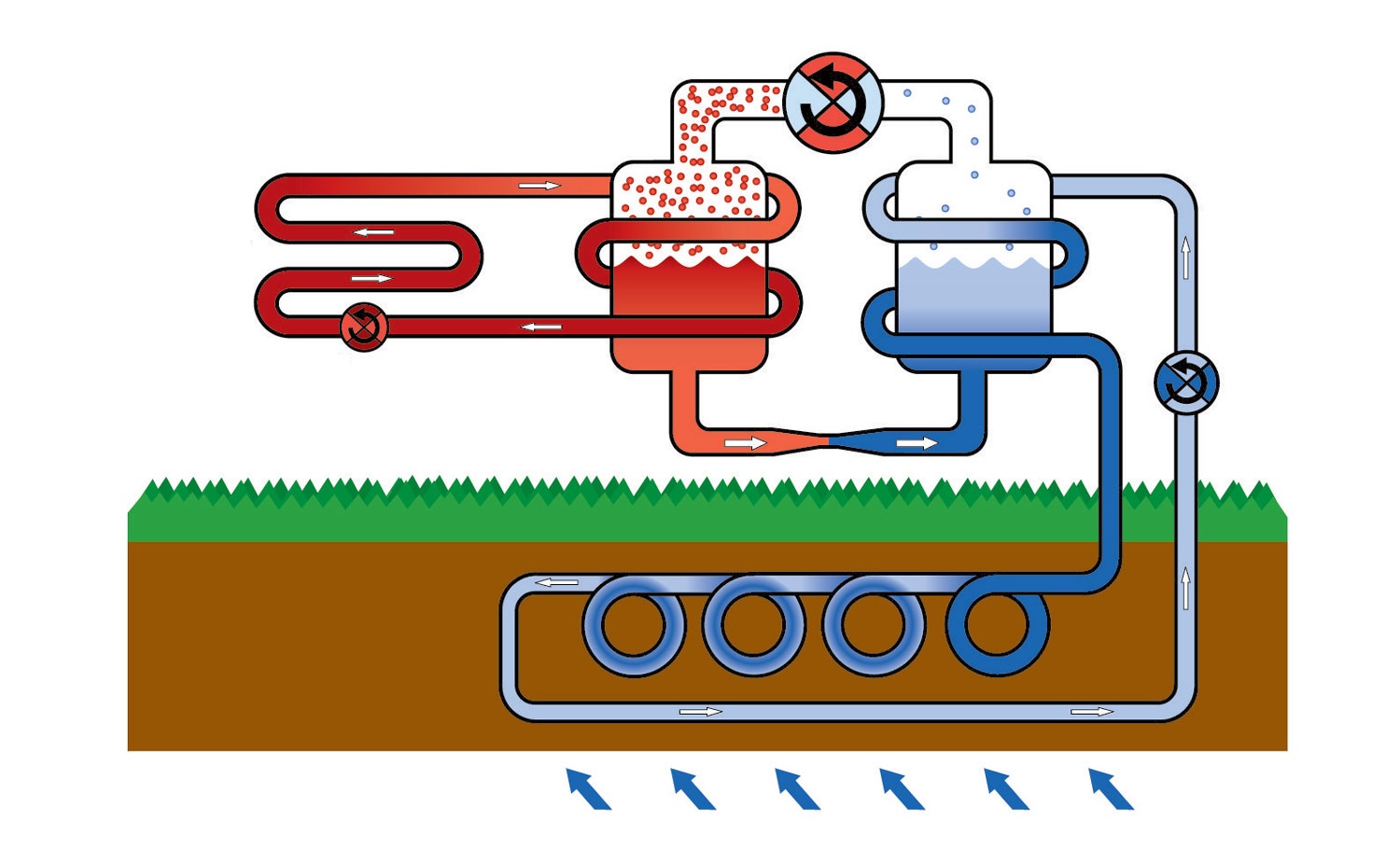
When classifying geothermal devices, the type of coolant in the heating system is also taken into account - water or air. Accordingly, the devices receive the designations "soil - water", "soil - air", "water - water", etc.
Video about heating
How to organize economical heating at home with your own hands, is described in the video below.
The logic of switching to alternative heating is not only to save money on buying gas or paying electricity bills.
Of course, non-renewable energy prices are skyrocketing. But how can one not recall the words of D. Mendeleev, who said: “Burning oil is the same as heating the stove with banknotes”?
It is unreasonable to burn tons of coal or tens of cubic meters of wood for the sake of heating a modest room and at the same time cause irreparable damage to the purity of the surrounding ecology.
In many countries, alternative types of heating and energy supply for an individual residential building are superior in demand to traditional methods of heating. The heating equipment market is filled with innovative alternative heating devices, the range of which is constantly expanding.
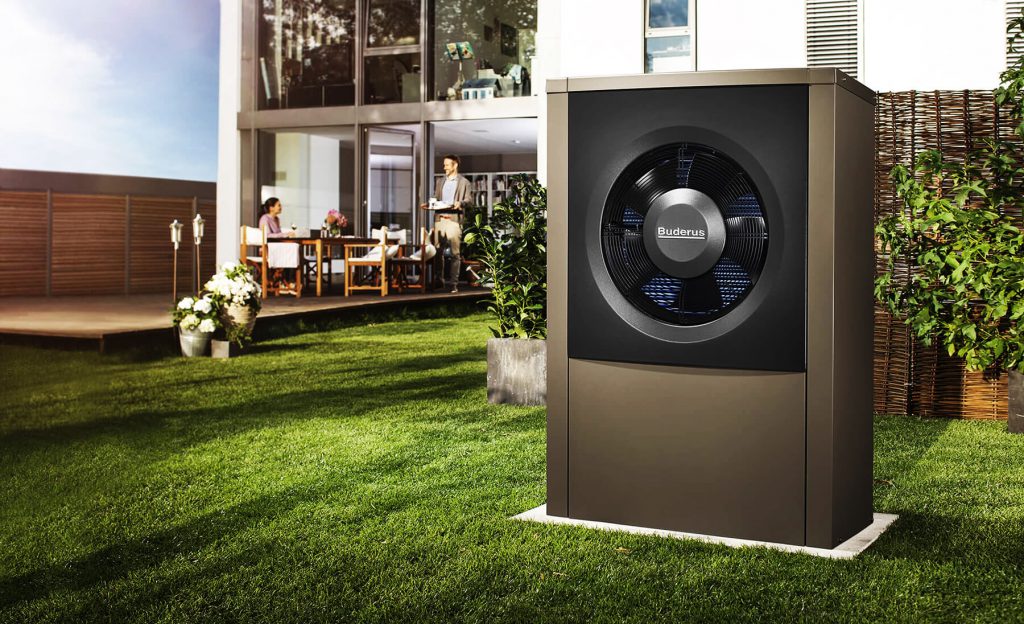 Air-to-water heat pump
Air-to-water heat pump In contact with