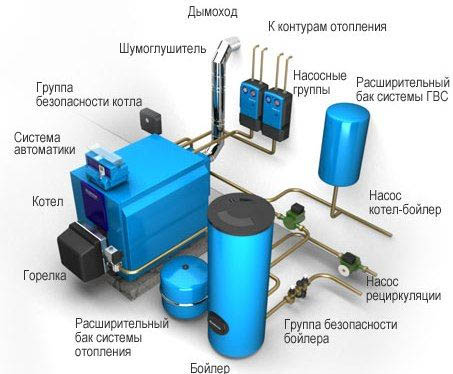
The most common way to obtain energy is the combustion of fossil fuels. To ensure it, it is necessary to supply oxygen to the combustion area. This problem is solved by continuous and sufficient ventilation of the room in which the heating boiler is installed. High-quality ventilation in the boiler room not only ensures the efficient operation of the autonomous heating system of a private house, but also saves the life and health of residents, as it prevents hazardous fuel combustion products from entering the residential area.
There are two types of ventilation: natural and forced. The first is the simplest, provided by open windows and vents, openings in and under doors, artificial drafts and air ducts in the walls. The forced system requires the use of a fan. It is inlet and outlet. In accordance with state rules and regulations, ventilation must be installed in the premises of a residential building, so their owners face the problem of choosing the optimal type. Both systems are successfully used in boiler rooms of private houses, but there are fundamental differences between them.
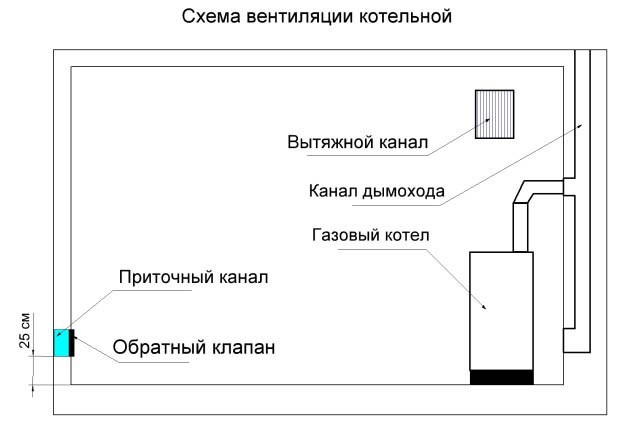
Natural ventilation is easier and cheaper to provide. It is enough to make an intake hole in the lower part of the outer wall, the diameter of which will depend on the power of the boiler and cannot be less than 15 cm. The air supply is regulated by a valve (stiber) mounted on the air duct. A hole is cut in the upper part of the wall to remove polluted air. It is noteworthy that natural ventilation for the boiler house is non-volatile, but critical to weather conditions and difficult to control.
For safety reasons, it is forbidden to install forced ventilation in the boiler room, since in the event of a boiler malfunction, combustible gas or fuel combustion products will enter the residential area of the house. Exhaust ventilation, which removes hazardous substances to the outside, in this case will serve as additional insurance. Forced systems allow you to flexibly control the climate in the premises of the house, but are volatile and expensive.
Basic requirements for ventilation
Most often, boilers for heating systems of cottages are installed in separate rooms - boiler rooms. Sometimes special extensions are created for them. In addition to fire safety standards, ventilation requirements must be met in order to ensure the flow of fresh air to the furnace and remove combustion products in a timely manner. The procedure for air exchange in rooms with various types of organic fuel is regulated by state norms and rules (SNiP). In case of non-compliance, the supervisory authorities will not give permission to operate.
Not surprisingly, the requirements for ventilation of a gas boiler house in a residential building are the most stringent. In this case, the danger for residents is not only harmful products of combustion, but also the fuel itself - gas. Softer conditions are put forward for the installation of low-power gas boilers (up to 30 kW). For them, it is not necessary to allocate a separate room, they can be installed in a residential area, for example, in the kitchen. The standards relevant for gas equipment are fully suitable for boilers using other types of fuel.
When installing ventilation, follow the rules:
1. The height of the ceilings in the room for heating equipment is not allowed to be lower than 6 m. Since it is literally difficult to fulfill this requirement in private households, it is possible to solve the problem by increasing the ventilation intensity of the boiler room. Each missing meter of height must be compensated by an increase in air exchange by 25%.
2. In addition, according to SNiP, ventilation should be provided in boiler rooms to ensure the complete replacement of three volumes of air in the room within 1 hour. This does not take into account the volume required to ensure the combustion of the boiler.
3. If natural ventilation cannot cope with the replacement of air in the boiler room, then it will be necessary to install a forced-type system.
Particular care and caution should be taken when designing high-rise building systems. A well-planned and well-installed supply ventilation in the boiler room of the cottage on 2 floors should supply the right amount of air to ensure the stable operation of the boiler, and the exhaust system should promptly remove exhaust gases to the outside through the common exhaust duct of the building.
Necessary calculations
Accurate and competent calculation of ventilation is an important stage in the design of a heating system. Professional engineering calculations take into account the dimensions of the furnace room, technical characteristics and the installation location of the equipment. Designing a boiler room of a private house is easier. You need to define the following parameters:
- The geometric dimensions of the room (length, width, height).
- Air flow rate. It should not be less than 1 m/s.
- The coefficient of air exchange amplification, due to the difference between the allowable height of the room (6 m) and its actual value.
- By multiplying the parameters of the room, its volume is calculated. It is equal to 33.6 m3.
- The coefficient of increase in the air exchange of the boiler room is determined: (6 - 2.8) * 0.25 + 3 = 3.8.
- The volume of air that must be replaced within an hour is found: V \u003d 3.8 × 33.6 \u003d 128 m³.
- The cross-sectional area of the channel, which must have exhaust ventilation in the boiler room of the cottage, is calculated by the formula: F = 128/3600 = 0.035 m2.
- The resulting area value is converted into diameter, since in practice circular ventilation pipes are more often used: D = 2 sqrt (S / π) = 211 mm.
Based on the found value, the exhaust pipe with the closest standard diameter (200 mm) is selected. The size of the inlet will also correspond to these parameters. In the engineering documentation, you can find ready-made tables for the selection of exhaust pipes, based on the required air flow.
DIY installation
A competent arrangement of the ventilation system of a boiler room includes three mandatory stages: preparation of a technical project, installation of equipment and performance testing. When planning, the performance of the ventilation unit, the length of the air ducts and the heat output of the boiler are taken into account. When installing air ducts, it must be remembered that their location depends on the type of air exchange used. Horizontal pipes should only be installed in forced-air systems. Moreover, their length is related to the capacity of the installed equipment. In any case, the channels should be straight, without bends or turns. Natural systems are allowed to be equipped only with vertical air views, the length of which cannot be less than 3 m.
Having completed the installation of the ventilation and heating system of a private house, it is necessary to check the performance of all its functional elements. It is required to make sure that there are no coolant leaks, reverse thrust and heat losses, measure the boiler efficiency and the concentration of carbon monoxide in the furnace. To ensure the reliability of measurements, they should be carried out only 24 hours after the start of heating and air exchange. In order to increase the safety of the boiler house and to effectively remove combustion products from it, it is useful to additionally use fire ventilation and a special smoke control system.