Bees play an important role in maintaining balance among other species and in their environment. In the case of the relationship between bees and people, these small insects are responsible for.
Why do people need bees?
.jpg)
One recent study shows that just 2 percent of wild bees pollinate 80 percent. This means that if this small percentage of bees disappears, 80 percent of our crops will die.
70 of the 100 most important food crops rely entirely on pollination - equivalent to 90% of the world's food.
It may sound incredible, but with the disappearance of bees, we can say goodbye to almonds, oranges and... Considering that about 850 million people around the world today suffer from lack of food... Plus, the population is increasing all the time, and by 2050 there will presumably be about 9 billion of us.

We need more and more bees if we are to avoid global food shortages.
Bees and the economy

The issue of food seems to be the most important, but the disappearance of bees will have a significant impact on the economy.
The same study led scientists to the conclusion that bees bring about $3,250 to the crop industry per hectare per year. The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations estimates that today around 1.4 billion hectares of land around the world are dedicated to growing crops.

Accordingly, these small insects contribute about $4.2 trillion to the global economy each year. dollars.
Bees' contribution to the ecosystem
Bees are extremely important not only in human life, but also in the functioning of the entire ecosystem. We all know that bees help flowers reproduce through pollination. These plants contribute to the food system by becoming food for birds and insects. If the food source for that part of the ecosystem disappears, the chain will be broken.
.jpg)
(Translation:"I'm hungry. Please grow flowers."
About 80 percent of flowers rely on pollination. If this process stops, we will not only lose the beautiful component of any natural landscape, but we will also lose food for ourselves, birds, squirrels and other living creatures.
Why are bees at risk?

One of the main threats facing bees is global warming and habitat changes. BUT. Pesticides kill bees more actively.
The Irony of Fate: people spray pesticides to grow crops, and these chemicals kill the bees that help these crops survive.

Neonicotinoids are a type of pesticide for bees. They attack the nervous system of insects, which almost always leads to instant death.

But some bees survive - and this option cannot be called lucky: the bees are lost in space and will never return home.
Good news: This type of pesticide has already been banned by the European Council and many stores in the US are also emptying their shelves of neonicotinoids in favor of bees.

There is still a long way ahead to the day when neonicotinoids will cease to be used on Earth altogether, but the process has already begun - this cannot but rejoice.
How can you help?

There are many options for what you can do as part of a bee rescue mission, the simplest ones are:
- Grow bee-friendly plants
- Support farmers, i.e. without the use of chemicals
- Spread this information around the world! Let more and more people know about the importance of bees in our lives.

Ministry of Education of the Republic of Kazakhstan
Department of Education, Physical Culture and Sports
General secondary school No. 24
Direction: ecology
Topic: “Once upon a time there was a bee...”
Completed:
student of grade 3 "B"
Zolotarev Andrey
Scientific adviser:
Abramova Tatyana Alexandrovna
primary school teacher
Secondary school No. 24, Balkhash
Balkhash 2014
annotation
Atalgan gylymi zhoba arany adam omirindegi paidasyn ashyp korsetedi. Zhumysta aranyn turleri, kurylysy tolyk korsetilgen. Airyksha konil baldyn emdik kasietterine bolingen.
This research project reveals the importance of bees to humans. In the work described bee species, their structure. Particular attention is paid to the healing properties of honey as the main waste product of bees.
Who are bees? ………………………………………………....... 4
The structure of a bee………………………………………………………. 5
Main types of bees………………………………………………………….. 5
Social and semi-social bees ………………… 6
Solitary bees………………………………………………………………. 6
Honey bees..…………………………………………… 7
Introduction…………………………………………………………………………………... 4
Main part ……………………………………………………………. 4
Honey ………………………………………………………………………………… 7
History of honey…………………………………………………….... 8
Interesting facts from the life of bees………………………………. 8
Conclusion ………………………………………………………………. 8
Appendix ………………………………………………………………………………… 9
List of references……………………………………... 10
Introduction
Bees are amazing creatures. They have existed for about 50 million years. Since time immemorial, people have appreciated the taste and, subsequently, the healing properties of honey. How highly valued this product was is evidenced by the fact that honey, as well as beeswax, were the main export items in Rus', for which they were paid in silver and gold. In Ancient Egypt, the bee served as a symbol of selflessness and fearlessness. She was depicted on the tombs of the first dynasty of pharaohs. The bee became a symbol of Lower Egypt. In ancient India, bees were considered companions of the gods. And in Ancient Greece, a bee was depicted on the coat of arms of the city of Ephesus.
Ever since people tried a unique and amazingly tasting product called honey, they have been preoccupied with how to train bees and use the waste products of these hardworking insects for their own benefit.
2. Main part
Who are bees?
Bees are insects that belong to the order Hymenoptera.
They can be found on all continents except Antarctica. Bees have adapted to feed on nectar and pollen, using nectar primarily as an energy source and pollen for protein and other nutrients.
Scientific classification of bees:
Kingdom: Animals
Type: Arthropods
Class: Insects
Squad: Hymenoptera
Suborder: Stalk-bellied
Superfamily: Bees
Bees are social insects, and therefore can only live as part of a bee family, in which each individual is assigned a specific function. In a bee colony, as a rule, there is one fertile queen (female), from several hundred to a thousand drones (males) and several tens of thousands of worker bees.
Bees have a long proboscis, which they use to suck nectar from plants. They also have antennae (or antennae, horns), each of which consists of 13 segments in males and 12 segments in females. All bees have two pairs of wings, the back pair being smaller in size than the front; only in a few species of one sex or caste the wings are very short, making the flight of the bee difficult or impossible.
The queen in a bee colony ensures the reproduction of offspring. Its main function is to lay eggs. The queen spends all her time inside the hive and lays eggs. The rest of the bees surround her with care and attention. And this is no coincidence, because without a queen the life of a bee colony is completely ruined. In one bee colony there is only room for one queen.
Drones are the male half of the bee colony. Their body is slightly wider than that of the queen and worker bees. The abdomen is rounded and the wings are powerful. Drones have good eyesight and sense of smell. Drones perform no other functions in the hive other than mating and maintaining optimal temperature.
Worker bees are females whose reproductive organs are underdeveloped, so they cannot mate. These individuals perform various functions in the bee family: they feed the larvae, bring water, pollen, and nectar to the hive, process nectar into honey, build honeycombs, and care for the queen and drones. Worker bees are smaller in size than the queen and drones, this feature allows them to fly quite long distances to collect nectar and pollen.
In addition to collecting nectar and pollen, bees perform a number of other functions. There are guard bees that protect the hive from the encroachment of other insects, animals, and thieving bees. Old bees also have responsibilities. They fly for water. This work is not considered hard.
Bees don't live long. Their lifespan depends on the time of hatching and working conditions. If the bee was hatched in the spring, then its life expectancy is 40-50 days. A bee that emerges in the summer, during the main feeding period, has a life cycle of 35-40 days, but if a bee hatches in the fall, after all seasonal work, then it lives for 8-9 months - until the next season.
Bee structure
The bee, like other insects, does not have a skeleton. To attach and protect internal organs, bees have a durable and flexible outer chitinous cover. Bees' legs and wings are made of chitin. All organs of a bee are ideally adapted to perform a variety of tasks, such as collecting food, caring for offspring, and pollinating plants. The entire body of a bee is covered with small hairs.
The body of a bee consists of sharply separated three parts: head, chest and abdomen, which are movably connected to each other.
Many species of bees are poorly studied. The size of bees ranges from 2.1 mm for the dwarf bee to 39 mm for a species found in Indonesia.
Social and semi-social bees
Main types of bees
Bees can live both independently of each other (that is, lead a solitary lifestyle) and exist in various social formations. The most advanced in this regard are social colonies, which are home to honey bees, bumblebees and non-stinging bees.
In some species, females of the same group are sisters to each other. If a group of bees has a certain division of labor, then such a group is called semi-social.
2.3.2.Single bees
Some bees are solitary bees in the sense that they have only one type of female that both reproduces and stores food for the young.
Solitary bees are important plant pollinators; the pollen they collect is used to feed their offspring. Often pollen is mixed with nectar, thus forming a paste-like mass.
Honey bees
Honey bees live in large families. Under normal conditions, a colony consists of one queen bee, many thousands of worker bees (females), and in the summer, drones (male bees living in a close community). Neither the queen bee, nor the worker bees, nor the drones can exist separately, nor can they independently form a new family.
There are about 20 thousand species of bees. They are distributed wherever there are flowering plants with which bees are closely associated.
All types of bees are useful as pollinators of most types of flowering plants, including cultivated ones (fruit trees and shrubs, legumes, buckwheat, etc.).
Honey
Honey is one of the most valuable food products. The bulk of honey, about 75-82%, is made up of fruit and grape sugar, precisely those types of sugar that are very easily absorbed by the human body. In addition to sugar, honey contains small amounts of proteins, iron, phosphorus and other substances that actively participate in bone growth and the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.Honey is nectar processed in the body of a bee. Processing consists in the fact that the substance that was collected from flowers is affected by enzymes of the gastric tract of the bee. The substance loses a large amount of water and acquires many useful properties. Honey is a mixture of sugar and other ingredients. The main components of honey are hydrocarbons, consisting of fructose (88.5%) and glucose (31%).
History of honey
Honey has been known to man since time immemorial. Even primitive people used it as a valuable food product and an effective remedy. The oldest rock paintings, which are more than 15 thousand years old, depict primitive “beekeepers” collecting honey.
Beekeeping was practiced in the ancient civilizations of Babylon, China, and India. Assyria in the 1st century. BC e. called the land of olive trees and honey. In Ancient Egypt, more than 3,500 years ago, honey was used as a delicacy, medicine, cosmetic drug and embalming agent.
The famous scientist Pythagoras claimed that constant consumption of honey helped him reach a ripe old age while maintaining clarity of mind. The ancient Greek philosopher Democritus, who lived more than 100 years, said that to maintain health, “the insides should be irrigated with honey, and the outside with oil.” The great thinker and patriarch of ancient medicine highly valued all products obtained by bees Hippocrates.
Interesting facts from the life of bees
Fact No. 1. To obtain one kilogram of honey, bees must make up to 4,500 flights and take nectar from 6-10 million flowers. A strong family can collect 5-10 kg of honey (10-20 kg of nectar) per day.
Fact No. 2. A bee can fly almost 8 km away from the hive and accurately find its way back. However, such long flights are life-threatening
bees and are unprofitable from the point of view of the productivity of its work.
Fact No. 3. The highest honey yields of nectar are obtained in the Far East and Siberia. There are known cases when, during the flowering period of linden in the Far East, the weight of the hive increased by 30-33 kg per day. Individual bee families in Siberia collect 420, and in the Far East - 330-340 kg of honey per season.
Fact No. 4. On a rough surface, a bee is capable of dragging a load that exceeds 320 times its body weight. For example, a horse carries a load equal to the weight of its own body.
Fact No. 5. Bees that have outlived their short life die in the hive only in winter, and in summer old bees, sensing the approach of death, leave the hive and die in the wild.
Fact No. 6. The queen bee never stings a person, even when he hurts her. But when she meets her rival, she furiously uses her sting.
Conclusion
Bees are the most important pollinators. The existence of many plant species sometimes depends on their pollinating function. To date, a rapid decline in bee populations has been observed in Europe and America, starting in the winter of 2006. The phenomenon of such a sharp extinction of bees was called “Bee Depopulation Syndrome” or “Colony Collapse Syndrome.” It manifests itself in the fact that worker bees suddenly leave their colonies and disappear. At the same time, even the corpses of bees are not found nearby.
This phenomenon has not been studied and has an unknown nature, but, according to many scientists, it is associated with genetic modifications of crops and the use of pesticides and other chemicals in the fields.
If the decline in bee populations continues at the same rate, these insects will disappear from the face of the earth by 2035. The disappearance of bees not only threatens the loss of honey, but also threatens the harvest of fruits, vegetables, berries, nuts and some grains. The pollination of many plants, and therefore their productivity, is entirely dependent on the activity of bees. One bee colony can pollinate about 3 million flowers in a day. In terms of efficiency, other insects cannot compare with bees.
Application.

Bibliography
Bondarev S.A., Romashki P.S. “Bees, honey, apiary”, Rostov-on-Don: Vlads, 2009.
“Encyclopedia of Animals”, Moscow: Eksmo, 2007.
G. M. Dlussky. " Life of Animals", vol. 3, Moscow: 1969.
The impact of urbanization on the environment. bee protection
The huge scale of urban and road construction, industrial processing of natural resources and chemicalization of agriculture have led to significant disturbances in the ecology of flora and fauna. According to N. Stoilov (Union of Beekeepers of Bulgaria, 1997), 98% of substances obtained in nature eventually turn into waste. Almost all of this mass pollutes the soil, water and air. In agriculture, about 5 billion tons of mineral fertilizers and 3 million tons of toxic substances, including pesticides, are used annually. All this does not pass without a trace for the bees. Moreover, it has been established that of all representatives of the animal world they are the most sensitive to environmental pollution. As a result of these reasons, in a number of once prosperous areas of beekeeping, this industry has fallen into decline.
Poisoning of bees on a large scale can occur due to industrial waste entering the atmosphere, spreading over 30 kilometers or more. It has been established that during the active period of life of bees, their death is most often observed during a decrease in atmospheric pressure and drizzling rains. Under such conditions, industrial waste, when distributed over long distances, intensively falls on plants.
Great damage to beekeeping is caused by waste from chemical, oil refineries, aluminum, phosphate, bauxite and brick factories. Magnesium dust is especially toxic to bees, exposure to which in certain regions leads to a complete cessation of beekeeping. Industrial wastes containing arsenic and carbon oxides, fluorine, hydrogen sulfide, phosphorus and chlorine compounds, lead, zinc, titanium and other elements are harmful and to a certain extent toxic to bees.
The harmful effects of industrial waste can manifest themselves in different ways. For example, arsenic oxide can accumulate in honey and bee bread, and bees poisoned by it die in late winter and early spring. The proximity of oil refineries leads to outbreaks of ascospherosis and increased death of queens.
The use of pesticides causes great harm to beekeeping. More than 350 chemicals are approved for use in agriculture. Let us recall that pesticides are divided into insecticides that act on harmful insects, herbicides that act on weeds, and fungicides that destroy pathogenic fungi. Of course, the use of these means, along with positive effects, also causes negative consequences. The use of pesticides leads to large losses of bee colonies, especially in those areas where notification of such actions is not established and penalties are not applied to violators.
From the book Recreational Fishing [with illustrations] author Kurkin Boris MikhailovichPROTECTION AND REPRODUCTION OF FISH RESERVES Currently, pristine reservoirs no longer exist or are almost gone. They are affected to one degree or another by human economic activity. The forms of its impact are fishing, hydraulic construction, increasing
From the book Fishing with Nets author Shaganov AntonThe influence of thread thickness on the catchability of the net When choosing net materials, in addition to the size of the net fabric and its meshes, it is worth paying attention to the thickness of the thread from which the net is knitted. When tying a fish, the thread from which the net is knitted cuts into the body of the fish and compresses it.
From the book Fishing Nets and Screens author Shaganov AntonThe influence of the thickness and color of the thread on the catchability of the net In addition to the size of the net fabric and its cells, it is worth paying attention to the thickness of the thread from which the net is knitted. When tying a fish, the thread from which the net is knitted cuts into the body of the fish and compresses it. The thinner the thread, the
From the book Encyclopedia of the Novice Driver author Khannikov Alexander Alexandrovich From the book Mistakes of Novice Motorists. Advice from experienced people author Gromakovsky Alexey Alekseevich From the book Warrior and Fishing Sports author Bernstein Semyon MarkovichChapter I PROTECTION AND REPRODUCTION OF FISH In recent years, the Communist Party and the Soviet government, in accordance with the decisions of the XXV Congress of the CPSU, have adopted a number of important documents on nature conservation and rational use of natural resources. Among them - o
From the book Guide to Spearfishing while holding your breath by Bardi Marco From the book Profitable Fish Farming author Zvonarev Nikolai MikhailovichThe influence of food on fish health Diseases often occur due to a poor food supply, the use of inferior artificial feed without the addition of microelements, vitamins, enzymes, antibiotics, amino acids and other elements, improper transportation and
From the book Beekeeping. Great encyclopedia author Korolev V.3 Beekeeping products, their properties and effects on health Beekeeping is certainly one of the oldest human activities. Its result is many valuable nutrients and medicinal substances - bee products, and above all honey. People recognized it and felt it for themselves
From the book Electronic Tricks for Curious Children author Kashkarov Andrey Petrovich6 Ecology, bee protection and foreign beekeeping
From the book The Basic Commandment author Fishchev Andrey From the book Mushroom Picker's Guide author Onishchenko VladimirThe influence of the process of studying a weapon on its survivability Not a single mechanism is designed for long-term operation in the study mode. This applies no less to weapons. Numerous idle descents, disassembly and reassembly, often performed in a non-standard manner,
From the book Joinery, carpentry, glass and parquet work: A practical guide author Kostenko Evgeniy MaksimovichChapter 6 Protection of mushrooms The protection of wild mushrooms should be considered from various points of view: it is necessary to protect rare, endangered species that are distinguished by their beauty, special shape, medicinal or nutritional properties. Below is a list of mushrooms growing in forests,
From the book 500 tips for a beekeeper author Krylov P. P.Chapter 7 OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH, SAFETY, ELECTRICAL SAFETY AT WOOD PROCESSING ENTERPRISES AND CONSTRUCTION 1. Occupational Safety The main components of occupational safety are: labor legislation, safety regulations and industrial sanitation.
From the author's book1. Labor protection The main components of labor protection are: labor legislation, safety precautions and industrial sanitation. Labor legislation regulates issues of labor law; safety precautions and industrial sanitation
Honey is an easily digestible food product. Although it consists mainly of simple sugars (80 - 84%) and water (16 - 20%), it includes up to 300 different components (enzymes, vitamins, salts, balms, etc.), which, together with the main part determine its dietary and medicinal properties. This product is widely used in the confectionery industry, cosmetics, and for the preparation of honey drinks. The medicinal nutritional and dietary properties of pollen, royal jelly and propolis are well known. A wide range of biological active substances are included in their composition, providing a biostimulating and tonic effect. Propolis is a strong antioxidant. Royal jelly, normalizing metabolism and the body's defenses, stimulating energy factors, stops the process of clogging body tissues with toxic pollutants and slows down the aging of the body. The role of bees in pollinating plants, including agricultural ones, is invaluable.
The role of bees is great as producers of specific products - honey, wax, pollen, royal jelly, propolis and bee venom. Each of them has a complex composition of substances that have a specific chemical effect. This allows them to be used in dietary practice for therapeutic purposes, especially for patients with immunological deficiency. Man has been using beekeeping products since ancient times. Nowadays, interest in them has in many cases grown significantly due to the economic importance of the products obtained from bees and their exceptional effect on the human body.
However, since the external environment is polluted, this affects the animal and plant world. Thus, when fuel is burned, harmful substances are released into the atmosphere, which reach the upper layers of the atmosphere, mix with water vapor and form sulfuric, sulfurous, nitric and nitrous acids, respectively. As a result, many species of mammals, birds, insects and other groups of animals are included in the Red Book. In particular, among insects these are the steppe and common bumblebees. At one time, Darwin noted that only these insects are capable of pollinating red clover flowers. That is why the disappearance of red clover as a species is associated with them, although we note that honey bees can also play the role of pollinators of plants of these species if they are trained appropriately. In an effort to obtain as much product as possible from crop areas, people influence the components of the ecosystem and especially the soil through the use of a set of agrotechnical measures, including chemicalization. There is intense contamination of the soil and atmosphere with radioactive substances; the greatest danger, as is known, is posed by two isotopes - strontium-90 (half-life 25 years), settling on the surface of the earth, and cesium-137 (half-life 33 years), accumulating in plants and soil through the circulation of substances.
By collecting nectar and pollen within a radius of 3 - 5 km from the apiary, bees also transfer all pollutants from the environment. When using contaminated nectar and pollen for their livelihoods, pollutants penetrate the body of insects. This leads either to the death of bees and their brood, or to a reduction in the life span of insects. We have repeatedly noted the weakening of such families.
Various chemicals entering the environment in the form of gaseous, liquid or solid particles are usually carried by bees into the hive with nectar, honeydew, pollen, tree resin, and water. Their concentration in a bee's nest can be 1000 - 100,000 times higher than in the air, and 1000 - 10,000 times higher than in plants. At the same time, this property makes the bee especially vulnerable to various pollutants. In a broad complex, reliable materials on the ecological characteristics of the area can be obtained from studies of the chemical composition of bees and beekeeping products. We conduct such studies in the south of the Tyumen region regularly.
When determining toxic elements in samples, we acted in accordance with GOST "Bee products. Mineralization of samples for determination of toxic elements." Mineralization is possible in two ways: dry - for all beekeeping products, except wax, and the acid extraction method for beeswax. For each beekeeping product, the indicated masses of samples were used to detect toxic substances by atomic adsorption and printing methods. The latter method is especially good, allowing you to detect several metals in one sample. Actual data on the detection of pollutants in apiaries in one of the districts of the Tyumen region are presented in the table.
Currently, quality control of products produced by bees in Russia is carried out in accordance with the requirements of regulatory and technical documentation for each type of product, hygienic requirements for the safety and nutritional value of food products (SanPin 2.3.2.1078-01).
There are no safety requirements for beeswax in these documents, since it is not classified as a food product. However, in our opinion, studies on the content of toxic substances in it should be carried out, since wax is in direct contact with beekeeping products, with brood, and besides, it is used in the perfume and pharmaceutical industries. The results of our research convince us of this: the accumulation of pollutants in the nests of bee colonies occurs precisely in wax. We attribute this to the fact that nest drying has been used for a number of years. We hope that further research to identify pollutants in various objects (soil and plants) will be continued. This will make it possible to draw up a scheme for the rational placement of apiaries in the region in order to ensure the production of truly environmentally friendly beekeeping products in the south of the Tyumen region.
Table1. Results of studies of soil samples, plants and bee products for contamination with heavy metals, radioactive substances and pesticides in apiaries in the Nizhne-Tavdinsky district of the Tyumen region
|
Indicators |
Plants |
|||||
|
detection |
||||||
|
Lead mg/kg |
Actual |
|||||
|
Error |
||||||
|
Cadmium mg/kg |
Actual |
|||||
|
Error |
||||||
|
Arsenic mg/kg |
Actual |
|||||
|
Error |
||||||
|
Cesium - 137 Bq/kg |
Actual |
|||||
|
Error |
||||||
|
Strontium-90 Bq/kg |
Actual |
|||||
|
Error |
||||||
|
HCH mg/kg |
Actual |
|||||
|
Error |
||||||
|
DDT mg/kg |
Actual |
|||||
|
Error |
||||||
S. A. Pashayan, Ph.D., Associate Professor,
Tyumen State Agricultural Academy
Dear visitor, you have entered the site as an unregistered user. We recommend that you register or log into the site under your name.
Heavy metals in nectaries and anthers of fireweed in residential areas
Oct, 2013
10
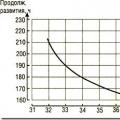
The perennial, cross-pollinated plant sainfoin has a high feeding value, is well eaten by livestock, and is an excellent honey plant. Its red-pink flowers are collected in thick long racemes. Violet veins are visible at the base of the flower flag, indicating the path to nectar for pollinators. According to research by V.K. Pelmenev and L.F. Kharitonova (1986), the nectary of a flower is located at the bottom of the flower tube.
Oct, 2013
08
International Convention on Biological Diversity
In 1992, in Rio de Janeiro (Brazil), Russia signed the Convention on Biological Diversity (http:/Avww.un.org/ru3Siary documen/convents/biodiv.htm), and ratified it in 1995.
The term “biological diversity” refers to the variability of living organisms, including within the same species. The signing of this international obligation was dictated by the realization “... lasting value biological diversity, as well as environmental, genetic, social, economic, scientific, educational, cultural, recreational and aesthetic significance.”
Sep, 2013
29
Honey bees are in danger
I remember the wonderful years of working with bees before 1978, when in the spring and summer the colonies grew and developed very rapidly. It happened that you would come to the apiary after a week-long break, and all the hives there were full of bees. And you begin to hastily expand your nests. And they developed this way because there was no varroatosis or ascospherosis, and the honey-bearing flora was richer and more diverse then.
Aug, 2013
30
Seed production of Siberian sainfoin

Aug, 2013
21
The main pests of honey bees in the Udmurd Republic
The life of bee families is closely connected with the environment. , like other representatives of fauna, natural predators and pests cause significant damage, knowledge of which will allow us to identify optimal measures to combat them and ensure higher profitability of the industry.
Aug, 2013
20
Attention - marten!
The village where the bees live is small and dying out. The gardens are running wild, overgrown with bird cherry and maple. Foxes, hares, and martens appeared. Two years ago I came to my bees at the end of March and saw this picture.