K category: Brickwork
Masonry methods
The laying of versts is carried out in three ways: pressing, butting and butting with cutting the mortar; and the forgetful ones are half-sitting. The choice of masonry method depends on the plasticity of the mortar, the condition of the brick (dry or wet), the time of year and the requirements for the cleanliness of the face of the masonry.
Using the pressing method (Fig. 1), brick walls are laid on a rigid mortar with full filling and jointing. This method is used to lay both spoon and butt versts. In this case, the solution is spread with a distance of 10-15 mm from the face of the wall. Level the mortar with the back of the trowel, moving it away from the laid brick and arranging a mortar bed for 3 spoon or 5 butt bricks at the same time. The laying is done in the following order. Holding a trowel in your right hand, level the mortar bed with it, then use the edge of the trowel to rake up part of the mortar and press it against the vertical edge of the previously laid brick, and with your left hand bring the new brick to the laying site. After this, the brick is lowered onto the prepared bed and, moving it with the left hand towards the previously laid brick, the trowel is pressed against the canvas. With an upward movement of the right hand, the trowel is removed, and with a brick moved with the left hand, the mortar is clamped between the vertical edges of the brick being laid and the previously laid one. Using hand pressure, the laid brick is settled on the mortar bed. Excess mortar, squeezed out of the seam onto the face of the masonry, is trimmed with a trowel in 1 step after laying every 3-5 bricks with pokes or after laying two bricks with spoons.
The solution is poured onto the mortar bed. The masonry is strong, with the joints completely filled with mortar, dense and clean. However, this method requires more movements than others and is therefore considered the most labor-intensive.
Using the butting method (Fig. 2), masonry is carried out using plastic mortars with incomplete filling of the joints with mortar along the face of the wall, that is, empty.
Rice. 1. Masonry using the method of pressing the spoon row of the outer mile: 1-4 - sequence of actions

Rice. 2. Masonry using the method of adjoining the spoon (a) and bond (b) rows of the outer mile: 1-3 - sequence of actions
The process of laying a spoon row with this method is performed in the following order. Taking a brick and holding it obliquely, use the butt edge of the brick to rake up part of the mortar previously spread on the bed. They begin to rake in the mortar at approximately a distance of 8-12 cm from the previously laid brick. Moving the brick towards the previously laid one, gradually straighten its position and press it to the bed. In this case, part of the mortar removed from the bed fills the vertical transverse seam. Having laid the brick, lay it down by hand on the mortar bed. When laying a bonded row, the laying process is carried out in the same sequence as a spoon row, only the mortar to form a vertical transverse seam is raked not with the bonder, but with the spoon edge.
Using this method, bricks can be laid with either the left or right hand.
To lay bricks using the back-to-back method, the mortar is spread in a bed with a distance of 20-30 mm from the outer vertical surface of the wall, so that during laying the mortar is not squeezed onto the front surface of the masonry. When constructing masonry in earthquake-prone areas, laying bricks in verst rows using the end-to-end method is not allowed.
The butt joint method with mortar cutting is used when constructing walls with complete filling of horizontal and vertical joints and with jointing of joints. In this case, the mortar is spread in the same way as when laying pressed, that is, with a distance of 10-15 mm from the face of the wall, and the brick is laid on the bed in the same way as when laying end-to-end.
The excess mortar, squeezed out of the seam onto the face of the wall, is trimmed with a trowel, as if pressed when laying. The mortar used for masonry is more rigid than for masonry without pruning. If the mortar is too plastic, the mason will not have time to cut it when squeezing it out of the masonry joints. More time and labor are spent on back-to-back laying with cutting mortar than on back-to-back laying, but less than on back-to-back laying.
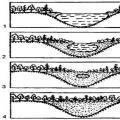
The backfill is laid out in a half-studded manner (Fig. 66). To do this, first spread a solution between the inner and outer versts. Then they level it, after which the brick is laid in the backfill. The process of laying backfill is simple.
During laying, the brick is held almost flat, at a distance of 6-8 cm from the previously laid one, gradually lowering the brick onto the mortar bed, raking in a small amount of mortar with an edge, moving the brick close to the previously laid one and pressing it into place with hand pressure. The vertical seams remain partially unfilled. They are filled when spreading the mortar for laying the next highest row, and the mason ensures that the transverse seams between the bricks are completely filled. Poor filling of vertical transverse joints with mortar not only reduces the strength of the masonry, but also increases the ventilation of the walls, which reduces their heat-insulating properties.
The backfill brick is pressed tightly to the bed so that the upper plane of the bricks laid in the backfill is at the same level as the benchmark ones.

Rice. 3. Laying the backfill using the half-stud method: a - with pokes; b - spoons; 1-2 - sequence of actions
- Laying methods
For many centuries, brick has been the most popular material for capital construction. Not all people know that there are different methods of bricklaying. Therefore, we will introduce you to this and other aspects.
What you need to know before starting work
You shouldn’t rush into battle and get to work right away. To get started, you should familiarize yourself with a few simple recommendations:
- In hot weather, water the brick. This will provide better adhesion to the cement.
- They cannot be used for laying plinths, as they do not have the required strength. It is also prohibited to use broken samples for the construction of pillars, because they do not meet the stated requirements. This rule also applies to the construction of foundations.
- To create stoves or fireplaces, it is best to use hollow products with increased heat. They are able to withstand severe heat without harming their structure. This property is achieved by adding special refractory clay.
- Splashes of solution must be removed immediately, because this will be problematic later. To do this, you can use a regular brush.
- It is prohibited to carry out masonry when the temperature is below +10 degrees. This can lead to the destruction of the solution and worsening the contraction.

- For outdoor work, only those samples that have frost resistance can be used. at least 50 cycles.
- During breaks in work, the structure should be covered with polyethylene.
- Store the brick in a place where it does not come into contact with the ground. This could harm him.
Preparation of the solution
All methods of laying bricks involve the use of mortar. Therefore, we will touch on this point as well.
First, you should familiarize yourself with the requirements for this component:
- The solution must have sufficient plasticity. This is necessary so that he can fill all the seams, irregularities and voids in the material.
- Its strength must be as high as possible so that after hardening it does not begin to deform. Otherwise, this will lead to destruction of the masonry.
- The setting time should be such that you can have time to apply it before it hardens completely. If you are doing masonry with your own hands for the first time, then the setting time should be at least 3 hours. After all, inexperienced people work much slower.
Cement has several varieties that differ in different characteristics. Therefore, its consumption for preparing the solution may also vary. In this regard, we present to your attention a table for preparing a composition using various brands of cement.

|
Cement brand |
Consumption (kg) per 1 cubic meter m. solution |
For 1 cu. m. sand |
Comparison of cement grades
You can use a ready-made frost-resistant solution, but its price will be much higher. However, if you start from the above recipe, you will be able to prepare a high-quality composition yourself.
Preparation of tools
The most important tool for a mason is Master OK(correct name - trowel). With its help, a number of operations are performed:
- Applying and leveling the solution.
- Creating grooves.
- Adjustment for bed.
Also important is a tool such as a pick-hammer, which is used for splitting and hewing bricks. If you plan to cut, you will also need a grinder with a diamond blade. With its help, you can accurately and quickly cut material.

You will also need masonry tools such as a level (to check the evenness of the masonry), a plumb line and a strong cord. In addition, it is advisable to get a concrete mixer to mix the solution. Today you can purchase a completely affordable product for private use.
Masonry methods
Today, four masonry techniques are actively used, which we will introduce you to. They have a number of features that, to one degree or another, affect the speed and quality of construction.
In the clamp
If we analyze all the methods of laying bricks, then “pressing” is the most labor-intensive, because it requires an impressive number of manipulations from the mason. However, it is rightly called the most durable and dense. At the same time, it is characterized by absolute filling of the seams.
This technique is most often used to build walls using rigid mortar. It is perfect for the construction of all types of structures.
So, it is done as follows:
- The mortar must be leveled using a trowel and used to create a “bed” designed for several bricks. Next, using the edge of the trowel, the excess mortar is separated and clamped to the upper edge.

- The first brick is lowered onto the applied and leveled mortar, close to the one placed earlier. Next, it is pressed as tightly as possible to the trowel. Then it is removed, and the remaining mortar is pressed between two adjacent bricks.
- Next, you should press on the installed brick so that it grips well and takes the correct position. In this case, you need to squeeze out the remaining mortar from the seams, which is trimmed with a trowel after installation. The remaining mortar is placed on a bed for laying other bricks.
Right in the middle
As the instructions say, this technique is prohibited in areas with increased seismic activity. It consists of the following:
- The brick is placed obliquely and a little mortar is scooped up with the butt edge within 10-12 cm.
- Then it is moved to the neighboring one, gradually leveling it out. After which he cuddles up to the bed. The solution removed from the bed is filled into the vertical seams.
Tip: laying the bonded rows is done in the same way.
- The installed brick is pressed tightly by hand.

Butt-together with trimming
If we compare all methods of laying facing bricks, then this method will have the best speed. It is applicable to any type of material, while allowing for complete filling of the seams.
Its main difference from the one indicated above is that the mortar is trimmed, similar to the “clamp” method. In this case, it is necessary to use a cement-sand composition that has increased mobility.
Half-baby
This method is applicable exclusively for laying in backfill. To implement this, the following is done:
- The mortar is spread and leveled between miles.
Then the brick is installed in the backfill. Experts recommend performing all operations with both hands, that is, laying two bricks at once, holding the second one at a slight distance from the installed one.
- By lowering it onto the bed, a certain amount of solution is scooped up. After which it is pressed against the already installed one. Vertical seams should be left incompletely filled.

Important! The zabutki must be pressed tightly against the mortar so that they are at the same level as the versts. At the same time, the seams must be filled well, because otherwise the structure will be blown through, which leads to deterioration of thermal protection.
Dressing methods
Now let's look at ways to bind brickwork, since this is also an important aspect. Bandaging is a laying method in which each brick rests on several lower ones. This allows for the best possible stability of the structure due to optimal load distribution.
Today, three methods are actively used, which we will introduce you to.
Chain (or single-row) method

The rows can be bonded or spooned. Bonded ones are when the brick is turned to the facade with the short side, and spooned ones, on the contrary. To help you better understand the difference, a visual diagram is presented above.
So, single-row dressing involves alternating both types of rows. This is a very reliable method that provides increased structural strength. As a rule, it is used for materials that do not require final finishing, that is, such as double sand-lime brick M 150.
To make it easier for you to understand, we present to your attention a visual diagram.

Using this technique, stock up on three-quarter bricks. They will be needed for laying ends, corners and pillars. It is not recommended to do this yourself, as it leads to time costs and damage to the material.
Modern production of ceramic bricks using the plastic method makes it possible to obtain scraps of the required size without time and labor costs. Therefore, many manufacturers are happy to sell them, which saves people from the need to cut.
Chain ligation at intersections
In this case, the dressing will have a number of features that need to be studied in order to avoid fatal mistakes. Please note that cutting can only be done with a grinder. Don't listen to people who say that you can simply split a brick.

Multi-row dressing
Involves diluting spoon rows with tyke rows. The main advantage of this method is that it does not require cut bricks.
The number of spoon rows is determined from the size of the building brick used. For samples 6.5 cm thick, 6 rows are used, the thickness 8.8 cm.
It is implemented as follows:
- The first row is placed in the same way as with a single-row dressing.
- The further course is determined based on the selected wall thickness. For walls that have a thickness equal to the fractional amount of brick (1\2, 3\2, etc.), masonry is carried out as follows:
- The outer mile of 3-5 rows is placed with a spoon, with dressing carried out on the 7th row.
- Internal versts are formed in row 2 with pokes, and in rows 3-6 with spoons. At the same time, we must not forget about bandaging the vertical seams on the brick floor.

Three-row dressing
It is a variation of the dressing described above. It consists of bandaging every three spoon rows. It is mainly used for the construction of pillars or piers.
It is worth noting that this technique gives the structure impressive strength. Its conditional diagram looks like this:

The first four rows of triple laying should look like this
Layout options
There is one more aspect that we will consider - this is the arrangement of the rows of masonry. After all, builders do not always use standard procedures. Of course, these varieties occur only when the brick is not subject to finishing.
So, there are six possible methods:
- "Track"- the simplest method, which is most often used by novice builders. Even small children know it, because this is how the Lego constructor is put together. In particular, it involves shifting each new row by half the length of the brick.
- "Blocky"- a more complex and, as a result, aesthetic arrangement option. To perform it you need to alternate whole and half bricks.
- Cross- consists of the same alternation as in the previous example. However, it also has its own significant difference: every second row must shift by half its length. The result is the appearance of a cross.
- Gothic– involves constant alternation of bricks of different lengths. As a result, the joints must be located one below the other. Moreover, in each odd row they must be offset by a distance equal to half their length.
- Brandenburg- involves alternating one short and two long bricks in all rows. The joints are located in the same way as in the previous example.
- "Savage"— an almost chaotic change of blocks of different lengths. Perhaps the most extraordinary technique.

Brickwork is produced in the following ways:
in the ranks- pressing, squeezing, squeezing with cutting of the solution;
in the backfill- solution method (half-filled).
Press the brickwork(Fig. 1) is carried out with the most complete filling of the seams. The mortar for the vertical seam is raked with a trowel, pressed against the previously laid brick and finally clamped with the brick being laid, while simultaneously pushing the brick down with the palm of the hand and aligning it along the mooring. The excess mortar squeezed out of the seam is trimmed with the edge of a trowel through several laid bricks.
Rice. 1. Brick laying pressed
End-to-end bricklaying(Fig. 2) is used when laying hollow walls and only with plastic mortar. The mason uses a trowel to level the spread mortar, and then uses the edge of a brick to rake up part of it to form a vertical seam, sets the brick down and aligns it along the pier. If the mortar is well laid and spread with a shovel, then the brick can be laid with one or two hands, without using a trowel. The brick is pressed down with the palm of the hand.
Rice. 2. Laying bricks end to end
Back-to-back masonry (Fig. 3) with seam trimming is used when laying full-seam walls, i.e., filling horizontal and vertical seams. A brick is laid on the spread mortar, raking the mortar with its edge to form a vertical seam. Moving the brick towards the previously laid bricks, the mason gradually straightens it, presses it to the bed, aligns it with the pier and sets it down. The excess mortar squeezed out of the seam is trimmed with the edge of a trowel every three to four bricks.
Rice. 3. Laying bricks end-to-end with seam trimming
Laying bricks in a backyard(half-squat) is performed with both hands (Fig. 4). The laying is carried out using a leveled mortar. Between the outer and inner versts, the mason uses the edges of bricks to rake in a small part of the mortar and pushes them down with hand pressure to the level of the previously laid versts. Partially unfilled vertical seams in the backfill are filled with mortar when spreading it for the next row.
Rice. 4. Laying bricks in a forgetful way
Masonry for jointing is carried out with complete filling of the seams with mortar. The masonry is carried out with cutting of the mortar. With the help of jointing, the seams of the masonry are given one shape or another. First, the vertical seams are unstitched, then the horizontal ones. Jointing ensures a more complete and uniform filling of the masonry seam.
Waste masonry is carried out when the front surface will be plastered or tiled. On the side of the surface to be plastered, vertical and horizontal seams are not filled with mortar to a depth of 10-15 m, which contributes to stronger adhesion of the plaster to
masonry. Vast laying is most often done using the end-to-end method.
There are three ways of laying versts - this is end-to-end bricklaying, press-on bricklaying, and end-to-end laying with cutting mortar. The laying of the backfill is carried out in a semi-filled position. When choosing a specific masonry method, it is necessary to take into account factors such as the condition of the brick (whether it is dry or wet), the plasticity of the mortar, the degree of required cleanliness of the face of the masonry, as well as the season of work.
Method of laying bricks pressed
Pressed brickwork is used for laying bricks on a rigid mortar with a cone draft of 7-9 centimeters with jointing and complete filling. The press-on method is suitable for laying both tie and spoon versts.
To install the clamp, you need to step back 10-15 millimeters from the front edge of the wall, fill it with mortar, and then level it with the back of the trowel. The trowel should be moved away from the laid brick so that at the same time a bed is formed for five interlocking and three spoon bricks. The sequence of actions when laying presses is as follows. Level the bed of mortar. The trowel should be held in the right hand. After this, rake up part of the mortar with the edge of the trowel and press the mortar against the vertical part of the already installed brick. With your left hand, take a new brick, lay it on a previously prepared bed of mortar and move it to the trowel blade located at the vertical edge of the previous brick. Then lift your right hand with a sharp movement to remove the trowel. Press the mortar between the vertical edges of the previously laid and new bricks, moving it with your left hand. The brick on the mortar bed must be settled with light pressure from the left hand. After laying 3-5 interlocking bricks, you should use a trowel to cut off the excess mortar from the front side of the masonry in one go. The excess is thrown onto the mortar bed again. This type of masonry is durable, clean and has completely filled seams. The disadvantages of pressing masonry include greater labor intensity, since with this method it is necessary to perform more movements.
Method of laying bricks end-to-end
Back-to-back masonry is used for plastic mortars (cone draft 12-13 centimeters). This is masonry with incomplete filling of the joints with mortar from the front part of the wall - empty space. Let's look at the procedure for laying the spoon row.
The solution is spread on the bed. The brick is taken and held in an inclined position. At a distance of about ten centimeters from the previously laid brick, with the butt side of the new one, you need to rake up a small part of the mortar, move it towards the already laid one, press it to the bed and level its position. In this case, the vertical transverse seam should be partially filled with mortar. The brick is laid down on the mortar bed by hand. The sequence of laying a row of interlocking bricks does not differ from the laying of a spoon row only in that the mortar for filling the vertical transverse seam in this case is raked not with the interfacing, but with the spoon edge. You can do end-to-end laying with either your right or left hand.
To avoid squeezing the mortar onto the front surface of the wall, the mortar should be spread on the bed, retreating 20-30 millimeters from the outer vertical surface of the masonry.
The butt joint method with mortar cutting is used when laying walls with full filling of joints, both horizontal and vertical, and with JUBOB jointing. By analogy with pressing masonry, the mortar is poured at a distance of 10-15 millimeters from the edge of the wall, and the brick is laid end-to-end. In this case, excess mortar is squeezed out of the seam onto the front side of the masonry. It is trimmed with a trowel in the same way as when laying pressed. In this case, the mortar used is more rigid (cone draft 10-12 centimeters), in contrast to the masonry option without trimming, since otherwise - with greater plasticity of the mortar - it will be problematic to have time to cut it off the face of the masonry. The back-to-back laying method with cutting the mortar requires more time and labor than the trimming option, but it is simpler than back-to-back laying.
Laying the backfill is done using the half-fill method.
The mortar is spread between the inner and outer verst masonry, then leveled - and you can begin to insert the forgetting. The masonry is quite simple. Take the brick and hold it at a distance of about eight centimeters from the one laid earlier. Slowly lower the brick onto the bed, rake a small amount of mortar with its edge, then press it tightly against the previously laid brick and press down with hand pressure.
Laying bricks in half-studs (a - splice; b - spoon)
With this method of laying, the vertical joints are not completely filled at first. They are completely filled with mortar from the top row of bricks. In this case, the transverse seams must be filled completely - this should be monitored during work.
When laying the zabutki, you need to press the bricks tightly against the bed so that the height of the zabutki row of household items is exactly at the same level as the milestone.
Currently, all over the world, including in Russia, such a branch of the national economy as construction is developing at a rapid pace. It has found wide application both in the construction of high-rise buildings, shops, and in private households. In the era of scientific and technological progress, there are many different building materials, and new ones are constantly being introduced. But one thing remains unchanged - the use of bricks in construction. It has been used for many decades. It is difficult to imagine such a craft without him. When erecting certain structures, you need to know the basic principles of laying it, the order of work, and the methods (methods) of laying bricks.

The quality and strength of the masonry depends on the properties of the bricks used, as well as on the mortar used and the professionalism of the craftsman.
The reliability of the design, the speed of operation and, accordingly, its quality are largely determined by which method (method) is used. There are ways, but not all of them are widely used in practice. It is important to note that any specialist must know all the techniques of this matter. Let us consider in more detail the basic methods of stone laying, the principles of masonry during construction, and the types of masonry. But before that, you need to know what bricks are and what they come in.
Definition, structure of the material

Brick is a man-made stone that is widely used in construction. It has good strength, frost resistance and water resistance. There are 3 main types of this material: fired clay (ceramic), silicate and hyper-pressed. These stones consist of 3 faces. They are called bed, spoon and poke. The first of them is the largest, it corresponds to the length of the brick. The spoon is a medium-sized edge located perpendicular to the bed, and the poke is the smallest of them. It is produced and used both as a whole, that is, in full-size form, and not. In the latter case, a third or half of it is applied.
Any mason needs to know that it is important to do preparatory work before laying the stone. When erecting any structure, the first step is to lay the foundation, then it is waterproofed and the masonry itself begins. These are the basic principles of construction, without which it is impossible to obtain good results. As mentioned above, the methods of laying it are very diverse. Let's look at some of them.

The main types of single-row suture ligation systems: spoon and chain.
Basic definitions
Most often, this material is laid in horizontal rows when it is laid flat. When constructing thin-walled structures, for example, walls, cornices, they can be laid sideways. Before studying masonry methods, you need to know the basic definitions so as not to get confused in the process itself. So, the first one is miles. Versts are the outermost rows that form the outer surface and border the environment. They can be external or internal. A spoon row is a row in which the stones are laid with the long side facing the outer surface of the wall. Bonded - a row facing outward with the short side. Zabutka are stones laid between the inner and outer versts.
Thus, you can easily get confused while working without knowing the most important concepts. In addition, you need to know that the height of the structure consists of the height of the stone, that is, next to it, and the height of the seams between them. Usually it is about 12 mm.
List of required tools

Schemes for laying bricks depending on the thickness of the wall that needs to be obtained.
For laying bricks you will need:
- spatula for spreading the solution;
- building level (it is necessary to determine the evenness of the structure);
- bricks;
- material for filling gaps between brick walls;
- container for stirring the solution;
- stretcher.
Direct masonry
Depending on which row of stone is being built, a certain masonry method is chosen.
For the construction of versts, 3 methods are used: pressing, butting, butting with cutting the mortar.
It’s best to put the scraps in a half-fill. The choice of one option or another depends on many factors, such as requirements for the cleanliness of the front side, time of year, conditions of the brick, plasticity of the mortar, and so on. Next, we will consider the dressing technique for brickwork. Brick walls with a rigid base are laid using the pressing method. It is carried out with full filling of the seams. With its help, brick laying of the spoon and butt parts is carried out. The solution is placed at a distance of 10 - 15 mm from the front surface of the wall.

Scheme of a multi-row suture ligation system.
Press masonry is done like this: hold a trowel in your right hand, level the bed with it, then partially rake up the mortar with the edge of the trowel and press it against the vertical part of the brick laid earlier, and lay a new stone with your left hand. Next, the brick is lowered onto the bed and pressed against the canvas with a trowel. Then take out the trowel with your right hand and clamp the mortar with a brick. Pressing with your hand, place the material on the solution. The excess is removed. The adjoining method is used for laying on plastic mortar. In this case, they take a brick, tilt it and rake in part of the mortar with the butt side. The solution is taken at a distance of 10 - 12 cm from the previously laid stone. While advancing it, they straighten the position and press it to the bed. It is important that the solution fills the joint. Next, the material is laid.
The butt-joint method with cutting the mortar

The main methods of laying bricks are: “tucked” and “pressed”. When laying "press" it is necessary to use a trowel (trowel).
It is relevant when it is planned to build a brick wall with full filling of the seams and jointing them. The mortar is laid out in the same way as when laying pressed, and the bricks are laid as in the end-to-end method, that is, it is like a mixed option, including the two above methods. In this case, it is advisable to use a more rigid solution. Trimming takes a lot of time, so in this case there will be more work than with conventional back-to-back laying. In addition to the above, there is another technique that is suitable for laying backfill. In this case, first of all, a solution is spread between the outer milepost and the inner one. The next stage is its leveling, after which the brick itself is laid.
The brick should be kept flat at a distance of approximately 6 - 8 cm from another that has already been laid. Then it is gradually lowered, moved towards the adjacent one and settled into place. It's quite simple. In addition, there is also a half-filled laying of the backfill. According to it, vertical seams may remain partially unfilled. This will happen when the solution is spread above the row located. Vertically located seams are filled completely. The strength of the wall depends on this, because its airflow increases. The backfill brick is pressed very firmly to the bed so that the top of the bricks in the backfill is at the same level as the milestone ones.
Laying dressing system
The brickwork dressing system is the order in which the stones are arranged relative to each other. The dressing system is not always given due attention. There are 3 types of dressing systems: for longitudinal seams, vertical and transverse. The first of the dressing systems is carried out so that the load on the wall during work is distributed evenly and so that it does not delaminate. A transverse ligation system is needed to establish a connection between the stones along their length. This dressing system is made using spoon or butt rows. The most common bonding systems in Russia are single-row, double-row or three-row brickwork bonding systems.

Main types of joints in brickwork. Their maximum thickness can be 12 mm.
With a single row, there is an alternation of spoon and butt rows. The transverse seams move approximately one-fourth of the brick, which ensures the stability of the structure. Longitudinal - half a stone. All vertical seams of the bottom row must be covered by the top row. What is characteristic of multi-row ligation is that the masonry consists of thin walls, a quarter of a brick wide, connected by bonded rows. In addition to the dressing system, the installation of brick pillars is also of great interest.
Construction of brick pillars

Pillars are classified depending on the number of bricks used in the brickwork. For example, a pillar of 1 brick, a pillar of 1.5 bricks.
The construction of pillars is most often used when laying a floor, when an underground is made between it and the ground. For such poles, it is very important to use high-quality material that will be resistant to moisture and must be durable. For brick pillars, it is important that the cross-section is equal to 1 stone. The construction of pillars is best done on a hard surface, preferably concrete. If one of the pillars is unevenly positioned, or if the soil around the pillars subsides, the floor may become uneven and sag, which sometimes poses a certain danger to residents. On the very first floor, a place for pillars is determined. It is better to do the laying of pillars together and using a single-row dressing, since single-row dressing is characterized by simplicity and efficiency of work.
The top of all brick pillars must be at the same level. Their evenness is checked with a lath or building level. An interesting fact is that the laying of brick pillars cannot use a multi-row ligation system, due to the fact that in this case the strength and solidity of the structure is not ensured. Therefore, laying brick pillars is a fairly simple matter, but at the same time requiring certain knowledge and skills.
Types of brickwork

Schemes for ordering brickwork with bandaging: for corners, pillars and at the junctions of walls.
In addition to simple bricks, other methods can be found in practice. These include well, brick and concrete anchor. The first is divided into lightweight and using different diaphragms. Lightweight masonry consists of 2 walls located at a distance of 140 to 340 mm from each other. They are connected to each other by transverse partitions. In this case, wells are formed, which are filled with expanded clay. In the second option, the longitudinal brick walls are tied in height with a diaphragm in five rows, that is, three horizontal rows.
Brick-concrete masonry is distinguished by the fact that it is represented by two walls half a brick thick, between which expanded clay concrete is placed. This structure provides good protection and strength, which is the most important thing in the construction craft.
Based on all of the above, we can conclude that bricklaying is a rather difficult task, for which you need to know the basic principles of bricklaying, what needs to be done to bind brickwork, what is required to erect brick pillars, and so on. The first thing that any specialist or ordinary worker needs to know and be able to do is that the foundation is laid first, since it is necessary to give the structure stability. It can be made of concrete or reinforced concrete. After this, waterproofing is installed, and at the end a wall or other brick structure is built.
There are several types of brickwork. Let's press the first one. The second end-to-end and the third end-to-end with trimming. They differ in many respects: filling the seams, laying the brick itself, and so on. In a broader sense, wall masonry can be divided into well masonry, anchor brick-concrete masonry and solid brick masonry. The latter is used most often. And is of great importance. It represents the relative position of the bricks relative to each other. Often in private construction you can see the construction of brick pillars. They are mainly used to make floor frames. For pillars, you cannot use low-quality building materials, including bricks that allow moisture to pass through.