Resolution of the State Committee of the Russian Federation
for construction and housing and communal services
On the adoption of building codes and regulations of the Russian Federation
"Labor safety in construction.
Part 2. Construction production"
The State Committee of the Russian Federation for Construction and Housing and Communal Sector decides:
1. Adopt and put into effect from January 1, 2003, the state construction norms and regulations SNiP 12-04-2002 "Labor safety in construction. Part 2. Construction production", presented by the Department of Economics and International Activities of the Gosstroy of Russia, developed by the Federal State Institution " Center for Labor Safety in Construction" of the State Construction Committee of Russia, the Analytical Information Center "Stroitrudobezopasnost", with the participation of the Central Research and Design-Experimental Institute of Organization, Mechanization and Technical Assistance to Construction.
2. To recognize as no longer valid on the territory of the Russian Federation from January 1, 2003, the USSR State Construction Committee Resolution No. 82 dated June 9, 1980 in terms of sections 8-18 SNiP III-4-80* “Safety in construction” with amendments No. 1- 5, as well as GOST 12.3.035-84 "SSBT. Construction. Painting works. Safety requirements", GOST 12.3.038-85 "SSBT. Construction. Work on thermal insulation of equipment and pipelines. Safety requirements" and GOST 12.3.040- 86 "SSBT. Construction. Roofing and waterproofing works. Safety requirements."
Chairman A. Shamuzafarov
Construction codes and regulations of the Russian Federation
OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY IN CONSTRUCTION
Part 2. CONSTRUCTION PRODUCTION
SNiP 12-04-2002
Date of introduction 2003-01-01
PREFACE
1 DEVELOPED by the Federal State Institution “Center for Occupational Safety and Health in Construction” of the Gosstroy of Russia (FGU TSOTS), the Analytical Information Center “Stroytrudobezopasnost” (AITs STB) with the participation of the Central Research and Design Experimental Institute of Organization, Mechanization and Technical Assistance to Construction (AOZT “ TsNIIOMTP")
INTRODUCED by the Department of Economics and International Activities of the Gosstroy of Russia
2. ADOPTED AND ENTERED INTO EFFECT from 01/01/2003 by Resolution of the State Construction Committee of Russia dated 09/17/2002 No. 123
3 INSTEAD of sections 8-18 SNiP III-4-80*, GOST 12.3.035-84, GOST 12.3.038-85, GOST 12.3.040-86
AGREED: Ministry of Labor of Russia (letter dated 03/03/2002 No. 5981-VYA)
FNPR (letter dated June 20, 2002 No. 109-85)
Registered by the Ministry of Justice of Russia on October 18, 2002 No. 3880
1 area of use
These rules and regulations apply to the production of general construction and special construction work performed during new construction, expansion, reconstruction, technical re-equipment, major repairs of buildings and structures (hereinafter referred to as construction production).
These rules and regulations use references to the regulatory legal acts given in Appendix A.
3. General provisions
3.1 The organization and performance of work in construction production must be carried out in compliance with the requirements of SNiP 12-03, PB 10-382 and other regulatory legal acts given in Appendix A, as well as these rules and regulations.
3.2 During the construction of facilities, measures must be taken to prevent workers from being exposed to hazardous and harmful production factors. If they exist, labor safety should be ensured on the basis of decisions contained in the organizational and technological documentation (POS, PPR, etc.), on the composition and content of the relevant requirements of SNiP 12-03 and these rules and regulations.
3.3 Before the start of construction of the facility, the general contractor must carry out preparatory work on organizing the construction site necessary to ensure construction safety, including:
arrangement of fencing of the construction site during the construction of an object in a populated area or on the territory of an organization;
clearing the construction site for the construction of the facility (clearing the area, demolishing buildings), planning the territory, drainage (if necessary, lowering the groundwater level) and relaying communications;
construction of temporary roads, laying temporary power supply networks, lighting, water supply;
delivery and placement on the construction site or outside of it of inventory of sanitary, industrial and administrative buildings and structures;
arrangement of crane tracks, storage areas for materials and structures.
The completion of preparatory work must be accepted according to the act on the implementation of occupational safety measures, drawn up in accordance with SNiP 12-03.
3.4 Work at the construction site should be carried out in technological sequence in accordance with the calendar plan (schedule) of work contained in the PIC. Completion of previous work is a necessary condition for the preparation and implementation of subsequent work.
If it is necessary to combine work, additional measures must be taken to ensure the safety of performing combined work.
3.5 Construction and installation work on the territory of an operating enterprise or a facility under construction must be carried out while carrying out the activities provided for by the approval certificate, the registration of which should be carried out in accordance with SNiP 12-03.
These measures are taken on the basis of decisions developed in the PIC and PPR, and include:
establishing the boundaries of the territory allocated to the contractor for work;
determining the procedure for admitting contractor employees to the organization’s territory;
carrying out the necessary preparatory work on the allocated territory;
determination of the area of combined work and the procedure for performing work there.
3.6 When several contractors, including citizens engaged in self-employment, work together at a construction site, the general contractor monitors the state of working conditions at the construction site.
If dangerous conditions arise at the site that pose a real threat to the life and health of workers, the general contractor must notify all construction participants about this and take the necessary measures to remove people from the danger zone. The resumption of work is permitted by the general contractor after the causes of the danger have been eliminated.
4. Dismantling of buildings and structures during their reconstruction or demolition
4.1 Organization of work
4.1.1 When dismantling buildings and structures (hereinafter referred to as dismantling buildings) during their reconstruction or demolition, it is necessary to take measures to prevent exposure of workers to the following hazardous and harmful production factors related to the nature of the work:
spontaneous collapse of structural elements of buildings and the fall of overlying unsecured structures, materials, and equipment;
moving parts of construction machines, objects moved by them;
sharp edges, corners, protruding pins;
increased content of dust and harmful substances in the air of the working area;
location of the workplace near a height difference of 1.3 m or more.
4.1.2 Before starting work on dismantling buildings, it is necessary to carry out preparatory measures related to the resettlement of citizens living in them or the departure of organizations located there, as well as disconnection from the networks of water, heat, gas and electricity, sewerage, technological product pipelines and taking measures against their damage.
All necessary approvals for preparatory activities must be made at the stage of developing the PIC.
4.1.3 The dismantling of buildings must be carried out on the basis of the solutions provided for in the organizational and technological documentation (POS, PPR, etc.). These solutions should be developed after conducting an examination of the general condition of the building (structure), as well as foundations, walls, columns, vaults and other structures. Based on the results of the survey, an act is drawn up, on the basis of which the following issues are resolved:
choosing a disassembly method;
establishing hazardous areas and using protective barriers if necessary;
temporary or permanent fastening or strengthening of the structures of a building being dismantled in order to prevent accidental collapse of structures;
dust suppression measures;
safety measures when working at height;
slinging diagrams for dismantling structures and equipment.
4.1.4 Before starting work, it is necessary to familiarize workers with the solutions provided for in the PPR and provide instructions on safe work methods.
Removal of unstable structures during building dismantling should be carried out in the presence of the work supervisor.
4.1.5 When dismantling buildings, access to them by unauthorized persons not involved in the work is prohibited. Work areas for dismantling buildings must be fenced in accordance with SNiP 12-03.
The passage of people into the premises during disassembly must be closed.
4.1.6 When dismantling buildings using a mechanized method, it is necessary to establish zones dangerous for people, and place machines (mechanisms) outside the zone of collapse of structures.
The driver's cabin must be protected from possible debris, and workers must be provided with safety glasses.
4.1.7 When dismantling buildings, as well as when removing waste and debris, it is necessary to take measures to reduce dust formation.
Those working in dusty conditions must be provided with respiratory protection against airborne dust and microorganisms (mold, fungi, their spores).
4.1.8 Before allowing workers into places with the possible appearance of gas or harmful substances, they must be ventilated. If gas appears unexpectedly, work should be stopped and workers should be removed from the danger zone.
Those working in places where gas may appear must be provided with protective equipment (gas masks).
4.2 Work procedure
4.2.1 Dismantling of buildings (dismantling of structures) must be carried out sequentially from top to bottom.
It is prohibited to dismantle buildings simultaneously in several tiers along the same vertical.
4.2.2 When dismantling buildings, it is necessary to leave passages to workplaces.
When dismantling the roof and external walls, workers must use a safety belt.
4.2.3 When dismantling cornices and hanging parts of the building, it is prohibited to stand on the wall.
It is not allowed to carry out work during ice, fog, rain that excludes visibility within the work front, thunderstorms and wind at a speed of 15 m/s or more.
4.2.4 When dismantling buildings, it is necessary to prevent spontaneous collapse or falling of structures.
Unstable structures located in the work area should be removed or secured, or strengthened in accordance with the PPR.
It is prohibited to cut chimneys, stone pillars and walls manually, or to collapse them onto the ceiling.
4.2.5 When dismantling buildings using the “felling” method, the length of the attached cables (ropes) must be 3 times the height of the building.
4.2.6 When dismantling buildings by explosive means, it is necessary to comply with the requirements of PB 13-407.
4.2.7 When dismantling structures and equipment using load-lifting cranes, it is necessary to comply with the requirements of Section 8 of these rules and regulations.
Methods of release, as well as slinging schemes for dismantled structures must comply with those provided for in the PPR.
4.2.8 Materials obtained from the dismantling of buildings, as well as construction waste, must be lowered through closed chutes or in closed boxes or containers using lifting cranes. The bottom end of the chute should be no higher than 1 m above the ground or enter the bunker.
Disposing of waste without chutes or other devices is permitted from a height of no more than 3 m. Dangerous areas in these places must be fenced off. The dimensions of the danger zone are established in accordance with SNiP 12-03.
4.2.9 Materials obtained during the dismantling of buildings must be stored in specially designated areas.
5. Excavation work
5.1 Organization of work
5.1.1 When performing excavation and other work related to placing workplaces in excavations and trenches, it is necessary to take measures to prevent exposure of workers to the following hazardous and harmful production factors related to the nature of the work:
falling objects (pieces of rock);
moving machines and their working parts, as well as objects moved by them;
location of the workplace near a height difference of 1.3 m or more;
increased voltage in an electrical circuit, the closure of which can occur through the human body;
chemically hazardous and harmful production factors.
5.1.2 In the presence of dangerous and harmful production factors specified in 5.1.1, the safety of excavation work must be ensured based on the implementation of the following labor protection decisions contained in the organizational and technological documentation (POS, PPR, etc.):
determination of the safe steepness of loose slopes of pits, trenches (hereinafter referred to as excavations), taking into account the load from machines and soil;
determination of the design of fastening the walls of pits and trenches;
selection of types of machines used for soil development and places of their installation;
additional measures to control and ensure slope stability due to seasonal changes;
determination of installation locations and types of fencing for pits and trenches, as well as stairs for descending workers to the work site.
5.1.3 In order to prevent soil erosion, the formation of landslides, and the collapse of the walls of excavations in places where excavation works are carried out, it is necessary to ensure the drainage of surface and groundwater before they begin.
The work site must be cleared of boulders, trees, and construction debris.
5.1.4 Excavation work in the security zone of high-voltage cables, an existing gas pipeline, other communications, as well as in areas with possible pathogenic contamination of the soil (landfills, cattle burial grounds, cemetery, etc.) must be carried out according to a permit after obtaining permission from the organization operating these communications or the sanitary inspection authority.
Work under these conditions should be carried out under the direct supervision of the work manager, and in the security zone of live cables or existing gas pipelines, in addition, under the supervision of employees of organizations operating these communications.
5.1.5 Development of soil in the immediate vicinity of existing underground communications is permitted only with the help of shovels, without the use of impact tools.
The use of earth-moving machines at the intersection of excavations with existing communications that are not protected from mechanical damage is permitted in agreement with the organizations that own the communications.
5.1.6 If communications, underground structures or explosive materials not specified in the project are discovered during excavation work, the excavation work must be suspended until permission from the relevant authorities is obtained.
5.2 Organization of workplaces
5.2.1 When placing workplaces in excavations, their dimensions, adopted in the design, must ensure the placement of structures, equipment, accessories, as well as passages at workplaces and to workplaces with a clear width of at least 0.6 m, and at workplaces - also the required space in the work area.
5.2.2 Excavations excavated on streets, driveways, in courtyards of populated areas, as well as in other places where people may be present, must be fenced with protective fences taking into account the requirements of state standards. Warning signs must be installed on the fence, and warning lights must be installed at night.
5.2.3 For the passage of people through excavations, transition bridges must be constructed in accordance with the requirements of SNiP 12-03.
To access work places in excavations, ladders or flight ladders with a width of at least 0.6 m with guardrails or ladders (wooden - no more than 5 m long) should be installed.
5.2.4 Work involving the presence of workers in excavations with vertical walls without fastening in sandy, silty-clayey and thawed soils above the groundwater level and in the absence of underground structures near them is allowed at their depth of no more than, m:
1.0 - in non-compacted bulk and natural sandy soils;
1.25 - in sandy loams;
1.5 - in loams and clays.
5.2.5 When the average daily air temperature is below minus 2C, it is allowed to increase the maximum depth of the vertical walls of excavations in frozen soils, except for loose frozen soils, compared to the value established in 5.2.4 by the depth of soil freezing, but not more than 2 m.
5.2.6 Work involving the presence of workers in excavations with slopes without fastenings in bulk, sandy and silty-clayey soils above the groundwater level (taking into account capillary rise) or soils drained by artificial dewatering is permitted depending on the depth of the excavation and the steepness slopes indicated in table 1.
Table 1
Item No. Types of soils Slope steepness (ratio of its height to foundation) at excavation depth, m, no more
1,5 3,0 5,0
1. Bulk uncompacted 1:0.67 1:1 1:1.25
2. Sand 1:0.5 1:1 1:1
3. Sandy loam 1:0.25 1:0.67 1:0.85
4. Loam 1:0 1:0.5 1:0.75
5. Clay 1:0 1:0.25 1:0.5
6. Loess 1:0 1:0.5 1:0.5
Notes: 1. When layering different types of soil, the steepness of the slopes is assigned according to the least resistant type from slope collapse;
2. Non-compacted fill soils include soils with a filling period of up to two years for sandy soils; up to five years - for silty-clayey soils.
5.2.7 The steepness of slopes of excavations with a depth of more than 5 m in all cases and a depth of less than 5 m under hydrological conditions and types of soil not provided for in 5.2.12, as well as slopes subject to moisture, must be established by the design.
5.2.8 The design of fastening the vertical walls of excavations up to 3 m deep in soils of natural moisture should, as a rule, be made according to standard designs. In case of greater depth, as well as complex hydrogeological conditions, the fastening must be carried out according to an individual project.
5.2.9 When installing fasteners, their upper part must protrude above the edge of the recess by at least 15 cm.
5.2.10 Before allowing workers into excavations with a depth of more than 1.3 m, the responsible person must check the condition of the slopes, as well as the reliability of fastening the walls of the excavation.
Boulders and stones, as well as loose soil found on slopes, must be removed.
5.2.11 The admission of workers into excavations with slopes that have been wetted is permitted only after a thorough inspection by the person responsible for ensuring the safety of the work, the condition of the soil of the slopes and the collapse of unstable soil in places where “peaks” or cracks (delaminations) are found.
5.2.12 Excavations developed in winter must be inspected upon the onset of a thaw, and based on the inspection results, measures must be taken to ensure the stability of the slopes and fastenings.
5.2.13 The development of excavations with vertical walls without fastening by rotary and trench excavators in cohesive soils (loams and clays) is allowed to a depth of no more than 3 m. In places where workers are required, fastenings must be installed or slopes developed.
When extracting soil from excavations using buckets, it is necessary to install protective canopies to protect those working in the excavation.
5.3 Work procedure
5.3.1 It is necessary to install fasteners in the direction from top to bottom as the excavation is developed to a depth of no more than 0.5 m.
5.3.2 It is not allowed to excavate soil in excavations. The soil removed from the excavation must be placed at a distance of at least 0.5 m from the edge of this excavation.
5.3.3 When developing excavations in the ground with a single-bucket excavator, the height of the face must be determined by the PPR in such a way that “peaks” of the soil do not form during the work.
5.3.4 When the excavator is operating, it is not allowed to carry out other work from the face and workers are not allowed to be within the radius of the excavator plus 5 m.
5.3.5 Dismantling of fasteners in recesses should be carried out from the bottom up as the recess is backfilled, unless otherwise provided by the PPR.
5.3.6 During mechanical impact loosening of soil, workers are not allowed to be at a distance closer than 5 m from the loosening sites.
5.3.7 One-sided backfilling of cavities during the construction of retaining walls and foundations is permitted in accordance with the PPR after measures have been taken to ensure the stability of the structure, under the accepted conditions, methods and order of backfilling.
5.3.8 When developing, transporting, unloading, leveling and compacting soil with two or more self-propelled or trailed machines (scrapers, graders, rollers, bulldozers), going one after another, the distance between them must be at least 10 m.
5.3.9 When unloading on embankments, as well as when backfilling excavations, dump trucks should be installed no closer than 1 m from the edge of the natural slope; Unloading from overpasses that do not have protective (fender) bars is prohibited.
The unloading locations for vehicles must be determined by the traffic controller.
5.3.10 It is prohibited to develop soil with bulldozers and scrapers when moving uphill or downhill, with an inclination angle greater than that specified in the machine’s passport.
5.3.11 The presence of workers and other persons in areas where soil compaction work is being carried out with free-falling rammers is not allowed, closer than 20 m from the base machine.
5.4 Special work methods
5.4.1 When developing quarries, it is necessary to comply with the requirements of regulatory documents of the Gosgortekhnadzor of Russia.
5.4.2 When developing rocky, frozen earthen soils using explosive methods, it is necessary to comply with the requirements of PB 13-407.
5.4.3 If it is necessary to use machines in difficult conditions (cutting soil on a slope, clearing rubble), you should use machines equipped with protective equipment that prevent workers from being exposed to hazardous production factors that arise in these conditions (falling objects and overturning).
5.4.4 In the case of electrical heating of the soil, the voltage of the power source should not be higher than 380 V.
The heated area of soil must be fenced off, safety signs installed on the fence, and illuminated at night. The distance between the fence and the contour of the heated area must be at least 3 m. Workers and other persons are not allowed to stay in the heated area.
5.4.5 Temporary power supply lines to heated areas of the ground must be made with insulated wire, and after each movement of electrical equipment and relocation of electrical wiring, the insulation resistance should be measured with a megohmmeter.
5.4.6 When developing soil using hydromechanization, the requirements of state standards must be met.
6. Construction of artificial foundations and drilling operations
6.1. Organization of work
6.1.1 When constructing artificial foundations and performing drilling operations, it is necessary to take measures to prevent exposure of workers to the following hazardous and harmful production factors related to the nature of the work:
collapsing rocks (soils);
moving machines and their working parts, as well as structures and objects they move;
location of workplaces near a height difference of 1.3 m or more;
overturning of cars, falling of piles and their parts;
increased voltage in an electrical circuit, the closure of which can occur through the human body.
6.1.2 In the presence of dangerous and harmful production factors specified in 6.1.1, the safety of the construction of artificial foundations and drilling operations must be ensured based on the implementation of the following labor protection decisions contained in the organizational and technological documentation (POS, PPR, etc.):
determination of methods and selection of mechanization means for carrying out work;
establishing the sequence of work;
development of a scheme for installation and dismantling of equipment, as well as its movement on the site;
determination of the range and required quantity of collective protective equipment necessary for use in the design of machines, as well as in the organization of workplaces.
6.1.3 Drilling operations and work on constructing artificial foundations should be carried out in compliance with the requirements of Section 5 of these rules and regulations.
6.1.4 Pile driving and drilling machines must be equipped with limiters for the lifting height of the drilling tool or load-handling device and an audible alarm.
6.1.5 Ropes must have a manufacturer’s certificate or a test report; lifting equipment must be tested and have tags or stamps confirming their load-carrying capacity and the date of testing.
6.1.6. The maximum weight of the hammer and pile for a pile driver, according to the machine’s passport, must be indicated on its truss or frame.
6.1.7 The distance between installed piling or drilling machines and buildings located near them is determined by the PPR. When operating these machines, a danger zone should be established at a distance of at least 15 m from the wellhead or the place where the pile is driven.
6.1.8 The movement of piling and drilling machines should be carried out along a pre-planned horizontal path when the machine structure is in the transport position.
6.1.9 When driving piles with a floating pile driver, it is necessary to ensure its reliable mooring to anchors fixed on the shore or at the bottom, as well as communication with the shore using duty vessels or a pedestrian bridge.
The floating pile driver must be provided with lifebuoys and a boat.
It is not allowed to carry out piling work on rivers and reservoirs with waves of more than 2 points.
6.1.10 Driving piles from ice is permitted only if there are special measures in the PPR to ensure the strength of the ice cover.
6.1.11 When work is stopped, drilled wells must be covered with shields or fenced. Safety warning signs and signal lighting must be installed on boards and fences.
6.1.12 Vibratory hammers must be equipped with suspended inventory platforms to accommodate workers who are attaching the head of the vibratory hammer to the shell.
The width of the platform deck must be at least 0.8 m. The platform deck must be fenced in accordance with the requirements of SNiP 12-03.
6.1.13 The inside walls of the sink well must be equipped with at least two securely fastened hanging ladders.
6.1.14 It is necessary to install protective canopies along the inner perimeter of the manhole. The dimensions, strength and installation procedure of the canopies must be determined in the PPR.
6.1.15 Premises where solutions for chemical fixation of soil are prepared must be equipped with ventilation and appropriate containers for storing materials.
6.2 Work procedure
6.2.1 Installation, dismantling and movement of piling and drilling machines should be carried out under the direct supervision of persons responsible for the safe performance of the specified work.
Installation, dismantling and movement of piling and drilling machines during winds of 15 m/s or more or thunderstorms are not allowed.
6.2.2 The technical condition of piling and drilling machines (reliability of fastening units, serviceability of connections and working decks) must be checked before the start of each shift.
6.2.3 Before lifting piling or drilling machine structures, their elements must be securely secured, and tools and loose objects must be removed.
When lifting a structure assembled in a horizontal position, all other work must be stopped within a radius equal to the length of the structure plus 5 m.
6.2.4 During the period of operation of piling or drilling machines, persons not directly involved in the performance of these works are not allowed to approach the machines at a distance of less than 15 m.
6.2.5 Before starting drilling or piling work, you must check:
serviceability of sound and light signaling devices, lifting height limiter of the lifting body;
the condition of the ropes for lifting mechanisms, as well as the condition of lifting devices;
serviceability of all mechanisms and metal structures.
6.2.6 Before inspecting, lubricating, cleaning or troubleshooting a drilling machine or pile driver, the drilling tool or pile driving mechanism must be lowered and placed in a stable position, and the engine stopped and turned off.
6.2.7 The lowering and raising of the drilling tool or pile is carried out after giving a warning signal.
While lifting or lowering a drilling tool, it is prohibited to perform work on the copter or drilling machine that is not related to the specified processes.
6.2.8 Lifting the pile (sheet pile) and the pile hammer must be carried out using separate hooks. If there is only one hook on the pile driver for installing the pile, the pile hammer must be removed from the hook and installed on a reliable locking bolt.
When lifting, the pile must be kept from swinging and torsion using braces.
Simultaneous lifting of the piling hammer and the pile is not allowed.
6.2.9 Piles are allowed to be pulled in a straight line within the visibility of the pile driver driver only through a tapping block fixed at the base of the pile driver. It is prohibited to pull piles with a pile driver to a distance of more than 10 m and with their deviation from the longitudinal axis.
6.2.10 When cutting piles driven into the ground, it is necessary to take measures to prevent the part being removed from suddenly falling.
6.2.11 Installation of piles and pile-driving equipment is carried out without interruption until they are completely secured.
Leaving them hanging is not allowed.
6.2.12 When driving piles using vibratory drivers, it is necessary to ensure a tight and reliable connection of the vibratory driver with the pile cap, as well as the free condition of the ropes supporting the vibratory driver.
6.2.13 The vibrator should be turned on only after it has been secured to the pile and the supporting pulleys have been loosened. The weakened state of the pulleys must be maintained throughout the entire operating time of the vibrator.
The vibrator should be turned off during every break in work.
6.2.14 When immersing shell piles, workers’ access to the suspended platform for attaching the head of a vibratory driver or the next section of the shell pile to the immersed shell pile is permitted only after the supplied structure has been lowered by a crane to a distance of no more than 30 cm from the top of the immersed shell pile. .
6.2.15 The sequence of soil development under the edge of the knife of the drop well should ensure its stability. The depth of soil development from the edge of the well knife is determined according to the PPR.
It is not allowed to develop soil below 1 m from the edge of the well knife.
6.2.16 When developing mobile soils with drainage or if there is a layer of such soils above the well blade, measures must be taken to ensure rapid evacuation of people in the event of a sudden breakthrough of the soil and flooding of the well.
6.2.17 Equipment and pipelines intended for performing work on soil freezing must be tested:
freezing station devices after installation - with pneumatic or hydraulic pressure specified in the passport, but not less than 1.2 MPa for the suction side and 1.8 MPa for the discharge side;
freezing columns before lowering into wells - with hydraulic pressure of at least 2.5 MPa.
6.2.18 Construction work in the area of artificial soil consolidation by freezing is permitted only after the ice-soil barrier reaches its designed thickness. Permission to carry out work must be formalized in an act.
6.2.19 Extracting soil from a pit that has an ice-soil barrier is permitted if the frozen wall is protected from rain and sunlight. When working, precautions should be taken to protect the ice-ground fencing from mechanical damage.
6.2.20 The procedure for monitoring the size and temperature of the ice-soil fencing of the pit during the process of freezing and thawing of the soil must be determined by the design.
6.2.21 Pipelines, hoses and injectors used for injection work on chemical consolidation of soils (silicatization, etc.) must be subjected to hydraulic tests with a pressure equal to one and a half working values, but not lower than 0.5 MPa.
6.2.22 Autoclave-type silicate cookers and other devices that are under pressure during operation must be subjected to regular technical inspections and periodic hydraulic tests in accordance with the requirements of the Gosgortekhnadzor of Russia.
... The full version of the document with tables, images and applications is in the attached file...
11 To prevent electric shock to workers, the following should be provided:
- instructions for the construction of temporary electrical installations, the selection of routes and determination of the voltage of temporary power and lighting electrical networks, devices for fencing live parts and the location of input distribution systems and devices;
- methods of grounding metal parts of electrical equipment;
- additional protective measures when performing work in high-risk and especially dangerous areas,
A also when performing work in similar conditions outdoors;
- measures for the safe performance of work in security zones and power lines.
12 To prevent workers from being exposed to harmful production factors (unfavorable microclimate, noise, vibration, dust and harmful substances in the air of the working area), it is necessary:
- identify areas of work where harmful production factors caused by technology may arise
And work conditions;
- determine means of protection for workers;
- provide, if necessary, special measures for the storage of hazardous and harmful substances.
13 Provide the necessary protective measures when using devices containing radioactive isotopes and serving as sources of ionizing radiation, as well as when using lasers.
SNiP 12-04-2002 “Labor safety in construction. Part 2 Construction production"
1 AREA OF USE
Regulatory documentation database: www.complexdoc.ru
These rules and regulations apply to the production of general construction and special construction work performed during new construction, expansion, reconstruction, technical re-equipment, major repairs of buildings and structures (hereinafter referred to as construction production).
IN These rules and regulations use references to regulatory legal acts given in the appendix A .
3. GENERAL PROVISIONS
3.1 The organization and execution of work in construction production must be carried out in compliance with the requirements SNiP 12-03, PB 10-382 and other regulatory legal acts given in Appendix A, as well as these rules and regulations.
3.2 During the construction of facilities, measures must be taken to prevent workers from being exposed to hazardous and harmful production factors. If they exist, labor safety must be ensured on the basis of the decisions contained in organizational and technological documentation (POS, PPR, etc.), on the composition and content of the relevant requirements of SNiP 12-03, these rules and regulations and other regulatory documents.
3.3 Before the start of construction of the facility, the general contractor must carry out preparatory work on organizing the construction site necessary to ensure construction safety, including:
- arrangement of fencing of the construction site during the construction of an object in a populated area or on the territory of an organization;
- clearing the construction site for the construction of the facility (clearing the area, demolishing buildings), planning the territory, drainage (if necessary, lowering the groundwater level) and relaying communications;
- construction of temporary roads, laying temporary power supply networks, lighting, water supply;
Regulatory documentation database: www.complexdoc.ru
- delivery and placement on the construction site or outside of it of inventory sanitary, industrial and administrative buildings and structures;
- arrangement of crane tracks, storage areas for materials
And designs. The completion of preparatory work must be accepted according to the completion certificate
occupational safety measures, formalized in accordance with SNiP 12-03.
3.4 Work at a construction site should be carried out
V technological sequence according to the contents
V POS calendar plan (schedule) of work. Completion of previous work is a necessary condition for the preparation and implementation of subsequent work.
If it is necessary to combine work, additional measures must be taken to ensure the safety of performing combined work.
3.5 Construction and installation work on the territory of an operating enterprise or a facility under construction must be carried out while carrying out the activities provided for by the approval certificate, the registration of which should be carried out in accordance with SNiP 12-03.
These measures are taken on the basis of decisions developed in the PIC and PPR, and include:
- establishing the boundaries of the territory allocated to the contractor for work;
- determining the procedure for admitting contractor employees to the organization’s territory;
- carrying out the necessary preparatory work on the allocated territory;
- determination of the area of combined work and the procedure for performing work there.
3.6 When several contractors, including citizens engaged in self-employment, work together at a construction site,
Regulatory documentation database: www.complexdoc.ru
The general contractor monitors the working conditions at the construction site.
If dangerous conditions arise at the site that pose a real threat to the life and health of workers, the general contractor must notify all construction participants about this and take the necessary measures to remove people from the danger zone. The resumption of work is permitted by the general contractor after the causes of the danger have been eliminated.
4. DISASSEMBLY OF BUILDINGS AND STRUCTURES DURING THEIR RECONSTRUCTION OR DEMOLITION
4.1 Organization of work
4.1.1 When dismantling buildings and structures (hereinafter referred to as dismantling buildings) during their reconstruction or demolition, it is necessary to take measures to prevent exposure of workers to the following hazardous and harmful production factors related to the nature of the work:
- spontaneous collapse of structural elements of buildings
And fall of overlying unsecured structures, materials, equipment;
- moving parts of construction machines, objects moved by them;
- sharp edges, corners, protruding pins;
- increased content of dust and harmful substances in the air of the working area;
and more.
4.1.2 Before starting work on dismantling buildings, it is necessary to carry out preparatory measures related to the resettlement of citizens living in them or the departure of organizations located there, as well as disconnection from the networks of water, heat, gas and electricity, sewerage, technological product pipelines and taking measures against their damage.
Regulatory documentation database: www.complexdoc.ru
All necessary approvals for preparatory activities must be made at the stage of developing the PIC.
4.1.3 The dismantling of buildings must be carried out on the basis of the solutions provided for in the organizational and technological documentation (POS, PPR, etc.). These solutions should be developed after conducting an examination of the general condition of the building (structure), as well as foundations, walls, columns, vaults and other structures. Based on the results of the survey, an act is drawn up, on the basis of which the following issues are resolved:
- choosing a disassembly method;
- establishing hazardous areas and using protective barriers if necessary;
- temporary or permanent fastening or strengthening of the structures of a building being dismantled in order to prevent accidental collapse of structures;
- dust suppression measures;
- safety measures when working at height;
- slinging diagrams for dismantling structures and equipment.
4.1.4 Before starting work, it is necessary to familiarize workers
With solutions provided for in the PPR, and provide instructions on safe work methods.
Removal of unstable structures during building dismantling should be carried out in the presence of the work supervisor.
4.1.5 When dismantling buildings, access to them by unauthorized persons not involved in the work is prohibited. Work areas for dismantling buildings must be fenced in accordance with SNiP 12-03.
The passage of people into the premises during disassembly must be closed.
Regulatory documentation database: www.complexdoc.ru
4.1.6 When dismantling buildings using a mechanized method, it is necessary to establish zones dangerous for people, and place machines (mechanisms) outside the zone of collapse of structures.
The driver's cabin must be protected from possible debris, and workers must be provided with safety glasses.
4.1.7 When dismantling buildings, as well as when removing waste and debris, it is necessary to take measures to reduce dust formation.
Those working in dusty conditions must be provided with respiratory protection against airborne dust and microorganisms (mold, fungi, their spores).
4.1.8 Before allowing workers into places with the possible appearance of gas or harmful substances, they must be ventilated. If gas appears unexpectedly, work should be stopped and workers should be removed from the danger zone.
Those working in places where gas may appear must be provided with protective equipment (gas masks).
4.2 Work procedure
4.2.1 Dismantling of buildings (dismantling of structures) must be carried out sequentially from top to bottom.
It is prohibited to dismantle buildings simultaneously in several tiers along the same vertical.
4.2.2 When dismantling buildings, it is necessary to leave passages to workplaces.
When dismantling the roof and external walls, workers must use a safety belt.
4.2.3 When dismantling cornices and hanging parts of the building, it is prohibited to stand on the wall. It is not allowed to carry out work during ice, fog and rain, excluding visibility within the work front, thunderstorms and wind at a speed of 15 m/s or more.
Regulatory documentation database: www.complexdoc.ru
4.2.4 When dismantling buildings, it is necessary to prevent spontaneous collapse or falling of structures.
Unstable structures located in the work area should be removed or secured, or strengthened in accordance with the PPR.
It is prohibited to cut chimneys, stone pillars and walls manually, or to collapse them onto the ceiling.
4.2.5 When dismantling buildings using the “felling” method, the length of the attached cables (ropes) should be 3 times the height of the building.
4.2.6 When dismantling buildings by explosive means, it is necessary to comply with the requirements PB 13-407.
4.2.7 When dismantling structures and equipment using cranes, it is necessary to comply with the requirements of Section 8 of these rules and regulations.
Methods of release, as well as slinging schemes for dismantled structures must comply with those provided for in the PPR.
4.2.8 Materials obtained from the dismantling of buildings, as well as construction waste, must be lowered through closed chutes or in closed boxes or containers using lifting cranes. The bottom end of the chute should be no higher than 1 m above the ground or enter the bunker.
Disposing of waste without chutes or other devices is permitted from a height of no more than 3 m. Dangerous areas in these places must be fenced off. The dimensions of the danger zone are established in accordance with SNiP 12-03.
4.2.9 Materials obtained during the dismantling of buildings must be stored in specially designated areas.
5. EARTHWORK
5.1 Organization of work
Regulatory documentation database: www.complexdoc.ru
5.1.1 When performing excavation and other work related to placing workplaces in excavations and trenches, it is necessary to take measures to prevent exposure of workers to the following hazardous and harmful production factors related to the nature of the work:
- falling objects (pieces of rock);
- moving machines and their working parts, as well as objects moved by them;
- location of the workplace near a height difference of 1.3 m
and more;
- increased voltage in an electrical circuit, the closure of which can occur through the human body;
- chemically hazardous and harmful production factors.
5.1.2 In the presence of dangerous and harmful production factors specified in 5.1.1, the safety of excavation work must be ensured based on the implementation of the following labor protection decisions contained in the organizational and technological documentation (POS, PPR, etc.):
- determination of the safe steepness of loose slopes of pits, trenches (hereinafter- notches) taking into account the load from the machines
and soil;
- determination of the design of fastening the walls of pits and trenches;
- selection of types of machines used for soil development and places of their installation;
- additional measures to control and ensure slope stability due to seasonal changes;
- determination of installation locations and types of fencing for pits and trenches, as well as stairs for descending workers to the work site.
5.1.3 In order to prevent soil erosion, landslides, and collapse of excavation walls in production areas
Regulatory documentation database: www.complexdoc.ru
Before excavation work begins, it is necessary to ensure the drainage of surface and groundwater.
The work site must be cleared of boulders, trees, and construction debris.
5.1.4 Excavation work in the security zone of high-voltage cables, an existing gas pipeline, other communications, as well as in areas with possible pathogenic contamination of the soil (landfills, cattle burial grounds, cemetery, etc.) must be carried out according to a permit after obtaining permission from the organization operating these communications or the sanitary inspection authority.
Work under these conditions should be carried out under the direct supervision of the work manager, and in the security zone of live cables or existing gas pipelines, in addition, under the supervision of employees of organizations operating these communications.
5.1.5 Development of soil in the immediate vicinity of existing underground utilities is permitted only with the help of shovels, without the use of impact tools.
The use of earth-moving machines at the intersection of excavations with existing communications that are not protected from mechanical damage is permitted in agreement with the organizations that own the communications.
5.1.6 If communications, underground structures or explosive materials not specified in the project are discovered during excavation work, the excavation work must be suspended until permission from the relevant authorities is obtained.
5.2 Organization of workplaces
5.2.1 When placing workplaces in excavations, their dimensions, adopted in the project, must ensure the placement of structures, equipment, accessories, as well as passages at and to workplaces with a clear width of at least 0.6 m, and at workplaces-also the required space in the work area.
5.2.2 Excavations developed on streets, driveways, courtyards of populated areas, as well as in other places where possible
Regulatory documentation database: www.complexdoc.ru
the presence of people must be protected by protective fences taking into account the requirements of state standards. Warning signs must be installed on the fence, and warning lights must be installed at night.
5.2.3 For the passage of people through excavations, transition bridges must be constructed in accordance with the requirements of SNiP 12-03.
To access work places in excavations, ladders or flight ladders with a width of at least 0.6 m with guardrails or ladders (wooden - no more than 5 m long) should be installed.
5.2.4
V recesses with vertical walls without fastening in sandy, silty-clayey and thawed soils above the groundwater level and in the absence of underground structures near them, it is allowed at their depth of no more than, m:
- 1.0 - in non-compacted bulk and natural sandy soils;
1.25 - in sandy loams;
- 1.5 - in loams and clays.
5.2.5 When the average daily air temperature is below minus 2 °C, it is allowed to increase the maximum depth of the vertical walls of excavations in frozen soils, except for loose frozen soils, compared to the value established in 5.2.4 by the depth of soil freezing, but not more than 2 m.
5.2.6 Carrying out work related to finding workers
V excavations with slopes without fastenings in bulk, sandy and silty-clayey soils above the groundwater level (taking into account capillary rise) or soils drained by artificial dewatering, is allowed at the excavation depth and slope steepness indicated in Table 1.
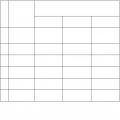
Table 1

Regulatory documentation database: www.complexdoc.ru
Slope steepness (ratio of its height to foundation) at excavation depth, m, no more
Types of soils
Bulk |
|||||
unpacked |
|||||
Sandy |
|||||
Loam |
|||||
Loess |
Notes: 1. When layering different types of soil, the steepness of the slopes is assigned according to the least resistant type from slope collapse;
2. Uncompacted fill soils include soils with a filling age of up to two years for sandy soils; up to five years - for silty-clayey soils.
5.2.7 The steepness of the slopes of excavations with a depth of more than 5 m in all cases and a depth of less than 5 m under hydrological conditions and types of soil not provided for 5.2.12, as well as slopes exposed to moisture, must be established by the project.
5.2.8 The design of fastening the vertical walls of excavations up to 3 m deep in soils of natural moisture should, as a rule, be made according to standard designs. In case of greater depth, as well as complex hydrogeological conditions, the fastening must be carried out according to an individual project.
5.2.9 When installing fasteners, their upper part should protrude above the edge of the recess by at least 15 cm.
Regulatory documentation database: www.complexdoc.ru
5.2.10 Before allowing workers into excavations with a depth of more than 1.3
m the responsible person must check the condition of the slopes, as well as the reliability of fastening the walls of the excavation.
Boulders and stones, as well as loose soil found on slopes, must be removed.
5.2.11 The admission of workers into excavations with slopes that have been wetted is permitted only after a thorough inspection by the person responsible for ensuring the safety of the work, the condition of the soil of the slopes and the collapse of unstable soil in places where “peaks” or cracks (delaminations) are found.
5.2.12 Excavations developed in winter must be inspected upon the onset of a thaw, and based on the inspection results, measures must be taken to ensure the stability of the slopes
and fastenings.
5.2.13 The development by rotary and trench excavators in cohesive soils (loams and clays) of excavations with vertical walls without fastening is allowed to a depth of no more than 3 m. In places where workers are required, fastenings must be installed or slopes developed.
When extracting soil from excavations using buckets, it is necessary to install protective canopies to protect those working in the excavation.
5.3 Work procedure
5.3.1 It is necessary to install fasteners in the direction from top to bottom as the excavation is developed to a depth of no more than 0.5 m.
5.3.2 It is not allowed to dig up soil in excavations.
The soil removed from the excavation must be placed at a distance of at least 0.5 m from the edge of this excavation.
5.3.3 When developing excavations in the ground with a single-bucket excavator, the height of the face must be determined by the PPR in such a way that “peaks” of the soil do not form during the work.
Regulatory documentation database: www.complexdoc.ru
5.3.4 When the excavator is operating, it is not allowed to carry out other work from the face and workers are not allowed to be within the radius of the excavator plus 5 m.
5.3.5 Dismantling of fasteners in recesses should be carried out from the bottom up as the recess is backfilled, unless otherwise provided by the PPR.
5.3.6 During mechanical impact loosening of the soil, workers are not allowed to be located at a distance closer than 5 m from the loosening sites.
5.3.7 One-sided backfilling of sinuses during the construction of retaining walls and foundations is allowed in accordance with the PPR after measures have been taken to ensure the stability of the structure, under the accepted conditions, methods and order of backfilling.
5.3.8 When developing, transporting, unloading, leveling and compacting soil with two or more self-propelled or trailed machines (scrapers, graders, rollers, bulldozers), going one after another, the distance between them must be at least 10 m.
5.3.9 Dump trucks when unloading on embankments, as well as when filling excavations, it should be installed no closer than 1 m from the edge of the natural slope; Unloading from overpasses that do not have protective (fender) bars is prohibited.
The unloading locations for vehicles must be determined by the traffic controller.
5.3.10 It is prohibited to develop soil with bulldozers and scrapers when moving uphill or downhill, with an inclination angle greater than that specified in the machine's passport.
5.3.11 The presence of workers and other persons in areas where soil compaction work is being carried out with free-falling compactors is not allowed, closer than 20 m from the base machine.
5.4 Special methods of work production
5.4.1 When developing quarries, it is necessary to comply with the requirements of regulatory documents of the State Mining and Technical Supervision of Russia.
Regulatory documentation database: www.complexdoc.ru
5.4.2 When developing rocky, frozen earthen soils using explosive methods, it is necessary to comply with the requirements PB 13-407.
5.4.3 If it is necessary to use machines in difficult conditions (cutting soil on a slope, clearing rubble), you should use machines equipped with protective equipment that prevent workers from being exposed to hazardous production factors that arise in these conditions (falling objects and overturning).
5.4.4 In case of electrical heating of the soil, the voltage of the power source should not be higher than 380 V.
The heated area of soil must be fenced off, safety signs installed on the fence, and illuminated at night. The distance between the fence and the contour of the heated area must be at least 3 m. Workers and other persons are not allowed to stay in the heated area.
5.4.5 Temporary power supply lines to heated areas of the ground must be carried out with insulated wire,
A After each movement of electrical equipment and re-wiring, the insulation resistance should be measured with a megohmmeter.
5.4.6 When developing soil using hydromechanization, the requirements of state standards must be met.
6. CONSTRUCTION OF ARTIFICIAL FOUNDATIONS AND DRILLING OPERATIONS
6.1 Organization of work
6.1.1 When constructing artificial foundations and performing drilling operations, it is necessary to take measures to prevent exposure of workers to the following hazardous and harmful production factors related to the nature of the work:
- collapsing rocks (soils);
- moving machines and their working parts, as well as structures and objects they move;
Regulatory documentation database: www.complexdoc.ru
- overturning of cars, falling of piles and their parts;
6.1.2 In the presence of dangerous and harmful production factors specified in 6.1.1. The safety of the installation of artificial foundations and drilling operations must be ensured on the basis of the implementation of the following labor protection decisions contained in the organizational and technological documentation (POS, PPR, etc.):
- determination of methods and selection of mechanization means for carrying out work;
- establishing the sequence of work;
- development of a scheme for installation and dismantling of equipment, as well as its movement on the site;
- determination of the range and required quantity of collective protective equipment necessary for use in the design of machines, as well as in the organization of workplaces.
6.1.3 Drilling operations and work on constructing artificial foundations should be carried out in compliance with the requirements of section 5 real rules and regulations.
6.1.4 Pile driving and drilling machines must be equipped with limiters for the lifting height of the drilling tool or load-handling device and an audible alarm.
6.1.5 Ropes must have a certificate manufacturer or their testing certificate; lifting equipment must be tested and have tags or stamps confirming their load-carrying capacity and the date of testing.
6.1.6 The maximum weight of the hammer and pile for a pile driver, according to the machine’s passport, must be indicated on its truss or frame.
6.1.7 Distance between installed piling or drilling machines and buildings located near them
Regulatory documentation database: www.complexdoc.ru
determined by the PPR. When operating these machines, a danger zone should be established at a distance of at least 15 m from the wellhead or the place where the pile is driven.
6.1.8 The movement of piling and drilling machines should be carried out along a pre-planned horizontal path when the machine structure is in the transport position.
6.1.9 When driving piles with a floating pile driver, it is necessary to ensure its reliable mooring to anchors fixed on the shore or at the bottom, as well as communication with the shore using duty vessels or a pedestrian bridge.
The floating pile driver must be provided with lifebuoys
And by boat. It is not allowed to carry out piling work on rivers and reservoirs with waves of more than 2 points.
6.1.10 Driving piles from ice is permitted only if there are special measures in the PPR to ensure the strength of the ice cover.
6.1.11 When work is stopped, drilled wells must be covered with shields or fenced. Safety warning signs must be installed on boards and fences
And signal lighting.
6.1.12 Vibratory hammers must be equipped with suspended inventory platforms to accommodate workers who are attaching the head of the vibrating hammer to the shell.
The width of the platform deck must be at least 0.8 m. The platform deck must be fenced in accordance with the requirements of SNiP 12-03.
6.1.13 The inside walls of the sink well must be equipped with at least two securely fastened hanging ladders.
6.1.14 It is necessary to install protective canopies along the inner perimeter of the sinkhole. The dimensions, strength and installation procedure of the canopies must be determined in the PPR.
6.1.15 The rooms where solutions for chemically fixing soil are prepared must be equipped
Regulatory documentation database: www.complexdoc.ru
ventilation and appropriate containers for storing materials.
6.2 Work procedure
6.2.1 Installation, dismantling and movement of piling and drilling machines should be carried out under the direct supervision of persons responsible for the safe performance of these works.
Installation, dismantling and movement of piling and drilling machines during winds of 15 m/s or more or thunderstorms are not allowed.
6.2.2 The technical condition of piling and drilling machines (reliability of fastening units, serviceability of connections and working decks) must be checked before the start of each shift.
6.2.3 Before lifting piling or drilling machine structures, their elements must be securely secured, and tools and loose objects must be removed.
When lifting a structure assembled in a horizontal position, all other work must be stopped within a radius equal to the length of the structure plus 5 m.
6.2.4 During the period of operation of piling or drilling machines, persons not directly involved in the performance of these works are not allowed to approach the machines at a distance of less than 15 m.
6.2.5 Before starting drilling or piling work, you must check:
- serviceability of sound and light signaling devices, lifting height limiter of the lifting body;
- the condition of the ropes for lifting mechanisms, as well as the condition of lifting devices;
- serviceability of all mechanisms and metal structures.
6.2.6 Before inspecting, lubricating, cleaning or troubleshooting a drilling machine or pile driver, the drilling tool or pile driving mechanism must be lowered and placed in a stable position, and the engine stopped and turned off.
Regulatory documentation database: www.complexdoc.ru
6.2.7 The lowering and raising of the drilling tool or pile is carried out after giving a warning signal.
While lifting or lowering a drilling tool, it is prohibited to perform work on the copter or drilling machine that is not related to the specified processes.
6.2.8 Lifting the pile (sheet pile) and the pile hammer must be carried out using separate hooks. If there is only one hook on the pile driver for installing the pile, the pile hammer must be removed from the hook and installed on a reliable locking bolt.
When lifting, the pile must be kept from swinging and torsion using braces.
Simultaneous lifting of the piling hammer and the pile is not allowed.
6.2.9 Piles are allowed to be pulled in a straight line within the visibility of the driver's driver only through a tapping block fixed at the base of the pile driver. It is prohibited to pull piles with a pile driver to a distance of more than 10 m and with their deviation from the longitudinal axis.
6.2.10 When cutting piles driven into the ground, it is necessary to take measures to prevent the part being removed from suddenly falling.
6.2.11 Installation of piles and piling equipment is carried out without interruption until they are completely secured.
Leaving them hanging is not allowed.
6.2.12 When driving piles using vibratory drivers, it is necessary to ensure a tight and reliable connection of the vibratory driver with the pile cap, as well as the free condition of the ropes supporting the vibratory driver.
6.2.13 The vibrator should be turned on only after it has been secured to the pile and the supporting pulleys have been loosened. The weakened state of the pulleys must be maintained throughout the entire operating time of the vibrator.
The vibrator should be turned off during every break in work.
Regulatory documentation database: www.complexdoc.ru
6.2.14 When immersing shell piles, workers’ access to the suspended platform for attaching the head of a vibratory driver or the next section of the shell pile to the immersed pile shell is permitted only after the supplied structure has been lowered by a crane to a distance of no more than 30 cm from the top of the immersed shell pile.
6.2.15 The sequence of soil development under the knife edge of the drop well should ensure its stability. The depth of soil development from the edge of the well knife is determined according to the PPR.
It is not allowed to develop soil below 1 m from the edge of the well knife.
6.2.16 When developing mobile soils with drainage or when there is a layer of such soils above the well blade, measures must be taken to ensure rapid evacuation of people in the event of a sudden breakthrough of the soil and flooding of the well.
6.2.17 Equipment and pipelines intended to perform soil freezing work must be tested:
- freezing station apparatus after completion of installation
- pneumatic or hydraulic pressure specified in the passport, but not less than 1.2 MPa for the suction side and 1.8 MPa for the discharge side;
- freezing columns before lowering into wells - with hydraulic pressure of at least 2.5 MPa.
6.2.18 Construction work in the area of artificial soil consolidation by freezing is allowed only after the ice-soil fencing reaches its designed thickness. Permission to carry out work must be formalized in an act.
6.2.19 Extracting soil from a pit that has an ice-soil fence is permitted if the frozen wall is protected from rain and sunlight. When working, measures should be taken to protect the ice-ground fencing from mechanical damage.
Regulatory documentation database: www.complexdoc.ru
6.2.20 The procedure for monitoring the size and temperature of the ice-soil fencing of the pit during the freezing process
And ground thawing must be determined by the project.
6.2.21 Pipelines, hoses and injectors used for injection work on chemical consolidation of soils (silicatization, etc.) must be subjected to hydraulic testing with a pressure equal to one and a half times the working pressure, but not lower than 0.5 MPa.
6.2.22 Autoclave-type silicate cookers and other devices that are under pressure during operation must be subjected to regular technical inspections and periodic hydraulic tests in accordance with the requirements of the State Mining and Technical Supervision Authority of Russia.
7. CONCRETE WORK
7.1 Organization of work
7.1.1 When preparing, supplying, laying and maintaining concrete, procuring and installing reinforcement, as well as installing and dismantling formwork (hereinafter referred to as concrete work), it is necessary to take measures to prevent workers from being exposed to hazardous and harmful production factors associated with the nature of the work:
- location of workplaces near a height difference of 1.3 m or more;
- moving cars and objects they move;
- collapse of structural elements;
Noise and vibration;
- increased voltage in an electrical circuit, the closure of which can occur through the human body.
7.1.2 In the presence of dangerous and harmful production factors specified in 7.1.1, the safety of concrete work must be ensured based on the implementation of the following labor protection decisions contained in the organizational and technological documentation (POS, PPR, etc.):
Regulatory documentation database: www.complexdoc.ru
- determination of mechanization means for preparing, transporting, supplying and laying concrete;
- determining the load-bearing capacity and developing a formwork design, as well as the sequence of its installation and disassembly order;
- development of measures and means to ensure workplace safety at heights;
- development of measures and means for the care of concrete in the cold and warm seasons.
7.1.3 When installing formwork, as well as installing reinforcement cages, you should be guided by the requirements of Section 8 “Installation work” of these rules and regulations.
7.1.4 Cement must be stored in silos, bunkers, chests
And other closed containers, taking precautions against spraying during loading and unloading. The loading openings must be closed with protective grilles, and the hatches in the protective grilles must be locked.
7.1.5 When using steam to heat inert materials located in bunkers or other containers, measures should be taken to prevent steam from penetrating into work areas.
The descent of workers into chambers heated by steam is allowed after the steam supply is turned off, as well as after the chamber and the materials and products contained in it have cooled to 40 °C.
7.2 Organization of workplaces
7.2.1 The placement of equipment and materials on the formwork that are not provided for by the PPR, as well as the presence of people not directly involved in the work on the installed formwork structures, are not allowed.
7.2.2 To transfer workers from one workplace to another, it is necessary to use stairs, transition bridges and gangways that meet the requirements SNiP 12-03.
Regulatory documentation database: www.complexdoc.ru
7.2.3 When installing prefabricated formwork for walls, crossbars and vaults, it is necessary to provide for the installation of working floors with a width of at least 0.8 m with fences.
7.2.4 The floor formwork must be fenced around the entire perimeter. All openings in the working floor of the formwork must be closed. If it is necessary to leave these holes open, they should be tightened with wire mesh.
7.2.5 After cutting off part of the sliding formwork and suspended scaffolding, the end sides must be fenced.
7.2.6 To protect workers from falling objects on suspended scaffolds, canopies should be installed along the outer perimeter of sliding and adjustable formwork with a width no less than the width of the scaffolding.
7.2.7 Walking on laid reinforcement is allowed only on special floorings with a width of at least 0.6 m laid on the reinforcement frame.
7.2.8 Removable lifting devices, slings and containers intended for supplying concrete mixture by lifting cranes must be manufactured and inspected in accordance with PB 10-382.
7.2.9 In areas where reinforcement is tensioned, in places where people pass, protective barriers with a height of at least 1.8 m must be installed.
Devices for tensioning reinforcement must be equipped with an alarm that is activated when the tensioner drive is turned on.
It is prohibited for people to stay within a distance of 1 m from reinforcing bars heated by electric current.
7.2.10 When using concrete mixtures with chemical additives, protective gloves and goggles should be used.
7.2.11 Workers laying concrete on a surface with a slope of more than 20° must use safety belts.
Regulatory documentation database: www.complexdoc.ru
7.2.12 The overpass for supplying concrete mixture by dump trucks must be equipped with fenders. Passages with a width of at least 0.6 m must be provided between fender bars and fences. Transverse fender bars must be installed on dead-end overpasses.
When cleaning the bodies of dump trucks from the remains of the concrete mixture, workers are prohibited from being in the body of the vehicle.
7.2.13 Preparation and enlarged assembly of reinforcement must be carried out in places specially designed for this.
7.2.14 The area where concrete is electrically heated must have a protective fence that meets the requirements of state standards, a light alarm and safety signs.
7.3 Work procedure
7.3.1 The operation of mixing machines must comply with the following requirements:
- cleaning pits for loading buckets should be carried out after the bucket is securely secured in the raised position;
- Cleaning the drums and troughs of mixing machines is allowed only after stopping the machine and relieving the voltage.
7.3.2 When performing work on the preparation of reinforcement, it is necessary to:
- install protective fences for workplaces intended for unwinding coils (coils) and straightening reinforcement;
- when cutting reinforcement bars with machines into sections less than 0.3 m long, use devices that prevent them from scattering;
- install protective fences for workplaces when processing reinforcement bars protruding beyond the dimensions of the workbench, and for double-sided workbenches, in addition, divide the workbench in the middle with a longitudinal metal safety mesh with a height of at least 1 m;
Regulatory documentation database: www.complexdoc.ru
- stack the prepared reinforcement in specially designated places;
- cover the end parts of the reinforcement bars with shields in places of common passages having a width of less than 1 m.
7.3.3 Elements of reinforcement frames must be packaged taking into account the conditions for their lifting, storage and transportation to the installation site.
7.3.4 Bunkers (tubs) for concrete mixture must meet the requirements of state standards. Moving a loaded or empty hopper is only permitted when the gate is closed.
7.3.5 When laying concrete from a bunker, the distance between the bottom edge of the bunker and the previously laid concrete or the surface on which the concrete is laid should be no more than 1 m, unless other distances are provided for by the PPR.
7.3.6 Every day, before starting to lay concrete in the formwork, it is necessary to check the condition of the container, formwork and scaffolding. Detected malfunctions should be corrected immediately.
Before starting to lay the concrete mixture with a vibrating robot, it is necessary to check the serviceability and reliability of fastening all its links to each other and to the safety rope.
7.3.7 When supplying concrete using a concrete pump, you must:
- carry out work on installation, dismantling and repair of concrete pipelines, as well as removing plugs from them only after the pressure has been reduced to atmospheric;
- remove all workers from the concrete pipeline at a distance of at least 10 m during purging;
- lay concrete pipes on spacers to reduce the impact of dynamic load on the reinforcement frame and formwork when supplying concrete.
7.3.8 Removing a plug in a concrete pipeline with compressed air is permitted provided:
Regulatory documentation database: www.complexdoc.ru
- the presence of a protective shield at the outlet of the concrete pipeline;
- workers are located at a distance of at least 10 m from the outlet of the concrete pipeline;
- supplying air into the concrete pipeline evenly, without exceeding the permissible pressure.
If the plug cannot be removed, the pressure should be relieved.
V concrete pipe, tap to find the location of the plug
V concrete pipe, uncouple the concrete pipe and remove the plug or replace the clogged link.
7.3.9 When installing formwork elements in several tiers, each subsequent tier should be installed after securing the lower tier.
7.3.10 Dismantling of the formwork should be done after the concrete reaches the specified strength.
The minimum strength of concrete during stripping of loaded structures, including from its own load, is determined by the PPR and agreed with the design organization.
7.3.11 When dismantling the formwork, it is necessary to take measures against accidental falling of formwork elements, collapse of supporting scaffolding and structures.
7.3.12 When moving sections of rolling formwork and mobile scaffolding, measures must be taken to ensure the safety of workers. Persons not participating in this operation are prohibited from being on sections of formwork or scaffolding.
7.3.13 When compacting a concrete mixture with electric vibrators, moving the vibrator by live cables is not allowed, and during breaks in work and when moving from one place. Otherwise, electric vibrators must be turned off.
7.3.14 When constructing technological holes for passing pipelines in concrete and reinforced concrete structures using diamond annular drills, it is necessary to fence off the danger zone at the site where the core is expected to fall.
7.3.15 When electrically heating concrete, installation and connection of electrical equipment to the power supply network should only be carried out
Regulatory documentation database: www.complexdoc.ru
electricians with a qualification group for electrical safety of at least III.
7.3.16 In the electrical heating zone, it is necessary to use insulated flexible cables or wires in a protective hose. It is not allowed to lay wires directly on the ground or over a layer of sawdust, as well as wires with damaged insulation.
7.3.17 The area where concrete is electrically heated must be under 24-hour supervision by electricians who are installing the electrical network.
The presence of workers and the performance of work in these areas is not allowed, with the exception of work performed under the permit in accordance with inter-industry rules on labor protection during the operation of electrical installations.
7.3.18 Open (non-concrete) reinforcement of reinforced concrete structures connected to the area under electrical heating is subject to grounding (zeroing).
7.3.19 After each movement of electrical equipment used when heating concrete to a new location, the insulation resistance should be measured with a megohmmeter.
APPENDIX A
List of regulatory legal acts referred to in these rules and regulations
1. SNiP 12-03-2001 "Occupational safety in construction. Part
1. General requirements." Adopted and put into effect by Resolution of the State Construction Committee of Russia dated July 23, 2001 No. 80. Registered by the Ministry of Justice of Russia on August 9, 2001 No. 2862.
2. PB 10-382-00 "Rules for the design and safe operation of load-lifting cranes." Approved by Resolution of the Gosgortekhnadzor of Russia dated December 31, 1999 No. 98. State registration is not required according to the letter of the Ministry of Justice of Russia dated August 17, 2000 No. 6884-ER.
3. PB 13-407 -01 "Unified safety rules for blasting operations." Approved by Resolution of the Gosgortekhnadzor of Russia dated January 30, 2001 No. 3. Registered by the Ministry of Justice of Russia on June 7, 2001 No. 2743.

Regulatory documentation database: www.complexdoc.ru
4. PB 03-428-02 "Safety rules for the construction of underground structures." Approved by Resolution of the Gosgortechnadzor of Russia dated November 1, 2001 No. 49. State registration is not required according to the letter of the Ministry of Justice of Russia dated December 24, 2001 No. 12467UD.
5. PPB 01 -93* "Fire safety rules in the Russian Federation." Approved by the Ministry of Internal Affairs of Russia on December 14, 1993 No. 536 as amended. and additional Registered by the Ministry of Justice of Russia on December 27, 1993 No. 445.
6. POT RM-010-2000 "Inter-industry rules for labor protection in the production of asbestos and asbestos-containing materials and products." Approved by Resolution of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated January 31, 2000 No. 10. They do not require state registration (letter of the Ministry of Justice of Russia dated March 22, 2000 No. 2029-ER).
INFORMATION AND REFERENCE APPENDIX
NAME OF REGULATIVE DOCUMENTS AND INFORMATION MATERIALS INTERRELATED WITH THESE STANDARDS AND RULES
Name |
|||||||||||
Name |
Official |
||||||||||
normative |
publisher |
||||||||||
normative act |
|||||||||||
act, date |
document |
||||||||||
statements |
|||||||||||
Gosstroy |
|||||||||||
"Safety |
|||||||||||
construction. Solutions for |
resolution |
||||||||||
industrial |
|||||||||||
security |
projects |
registered |
|||||||||
construction organization |
|||||||||||
and projects |
made in Russia |
||||||||||
23407-78conditions" |
|||||||||||
"Unified Gosgortekhnadzor State Unitary Enterprise STC |
|||||||||||
safety rules in Russia, |
Gosgortekhnadzor |
||||||||||
mining decree |
|||||||||||
useful |
fossils from 07/21/92 No. 20 |
||||||||||
open way" |
editorial office in Russia |
||||||||||
resolutions |
|||||||||||
dated 10/31/97 No. 39) |
|||||||||||
Gosstroy |
|||||||||||
Production |
|||||||||||
earthen |
way |
resolution |
|||||||||
hydromechanization. |
from 01.21.02 No. 5 |
||||||||||
Safety requirements" |
|||||||||||
21807 -78 |
"Bunkers Gosstroy |
||||||||||
portable Russia, |
|||||||||||
capacity up to 2 m3 for regulation |
|||||||||||
concrete |
mixtures. General from 04/28/76 No. 59 |
||||||||||
technical specifications" |
|||||||||||
RM-016-2001/RL Ministry of Labor |
|||||||||||
153-34.0-03.150-00 |
|||||||||||
Set of RULES SP 48.13330.2011
“SNiP 12-01-2004. Organization of construction"
(approved by order Ministry of Regional Development of the Russian Federation dated December 27, 2010 No. 781)
1 Application area
This set of rules applies to the construction of new, reconstruction and demolition of existing buildings and structures (hereinafter referred to as construction), erected on the basis of a construction permit obtained in the prescribed manner, as well as to the improvement and engineering preparation of territories.
During the construction of linear structures, power lines, communications, pipelines and other technical infrastructure facilities, as well as in the right of way of railways, in the right of way of roads and other transport routes, the requirements of current regulatory documents must be additionally taken into account.
In relation to military infrastructure facilities of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation, facilities, information about which constitutes a state secret, facilities for the production, processing, storage of radioactive and explosive substances and materials, facilities for the storage and destruction of chemical weapons and explosive means, and other facilities for which requirements are established related to ensuring nuclear and radiation safety in the field of atomic energy use, the requirements established by state customers, federal executive authorities authorized in the field of ensuring the safety of these facilities, and government contracts (agreements) must be observed.
The document does not apply to buildings and structures, the construction of which is in accordance withlegislationon urban planning activities can be carried out withoutpermissionsfor construction, as well as for individual housing construction projects erected by developers (individuals) on their own, including with the involvement of hired workers, on land plots owned by them.
The document also does not apply to the production of materials, products and structures at enterprises in the construction industry and the building materials industry.
This set of rules uses references to regulatory legal acts given inAppendix A.
3 Terms and definitions
This set of rules mainly adopts terms and definitions forTechnical regulationson the safety of buildings and structures.
4 General provisions
4.1 The construction of buildings and structures is carried out in the presence of a construction permit obtained in accordance with the legislation on urban planning activities.
Lists of buildings and structures for the construction of which a construction permit is not required are established by the legislation on urban planning activities.
4.2 The actions of construction participants, the work performed during the construction process, their results, including completed buildings and structures, must meet the requirements of current legislation, design and working documentation, and urban planning plans for land plots.
4.3 The developer must ensure the performance of all functions specified in 4.4, 4.6 and not assigned by agreement to other construction participants.
4.4 The basic functions of the developer are:
- obtaining a construction permit;
- obtaining the right of limited use of neighboring land plots (easements) for the duration of construction;
- engaging a contractor (general contractor) to carry out work on the construction of a building or structure as a person carrying out construction, in the case of carrying out work under a contract;
- providing construction with design documentation that has undergone examination and approved in the prescribed manner;
- ensuring the setting out of building control lines and creating a geodetic alignment basis:
- engaging, in accordance with 7.4, designer's supervision of the person who prepared the design documentation for the construction of the facility;
- notification of the start of any work on a construction site to the state construction supervision body that controls the facility;
- ensuring construction control of the developer (customer);
- acceptance of a completed construction project in the event of work being carried out under a contract;
- organizing setup and testing of equipment, trial production of products and other activities to prepare the facility for operation;
- making decisions on the start, suspension, conservation, termination of construction, on the commissioning of a completed property;
- presentation of the completed construction project to the authorities of state construction supervision and environmental supervision (in cases provided for by the legislation on urban planning activities);
- presentation of the completed construction project to the authorized body for commissioning;
- compilation, storage and transfer of executive and operational documentation to the relevant organizations.
4.5 The developer to carry out its functions of providing construction with design documentation that has been examined and approved in the prescribed manner, upon obtaining a construction permit, its functions as a customer during construction on the basis of a contract, to carry out construction control of the customer, as well as to interact with state supervisory authorities and local government may attract, in accordance with current legislation, a specialized organization or specialist with appropriate qualifications.
The transfer by the developer of its functions to an involved organization or specialist is formalized by an agreement between them.
4.6 When carrying out construction on the basis of a contract, the basic organizational functions of the contractor (general contractor) as the person carrying out the construction are:
- execution of works, structures, engineering and technical support systems for the construction site in accordance with design and working documentation;
- development and application of organizational and technological documentation:
- implementation of construction control of the person carrying out the construction, including control over the compliance of the building materials and products used with the requirements of technical regulations, design and working documentation;
- maintaining executive documentation;
- ensuring labor safety on the construction site, safety of construction work for the environment and the population;
- construction site management, including ensuring the security of the construction site and the safety of the object until its acceptance by the developer (customer);
- fulfilling the requirements of the local administration, acting within its competence, to maintain order in the territory adjacent to the construction site.
- 4.7 The basic function of the person who prepared the design documentation (hereinafter referred to as the designer) during the construction process is to introduce, in accordance with the established procedure, changes to the design estimates and working documentation in the event of changes after the start of construction of the urban planning plan of the land plot or existing regulatory documents (performed as an additional work).
- Additional organizational functions of the designer during the construction process, performed in accordance with agreements between construction participants, are:
- making changes to design and estimate documentation
due to the need to take into account the contractor’s technological capabilities;
- development of additional design solutions in connection with the need to ensure production;
Coordination of deviations from working documentation, including making decisions on the possibility of using non-conforming products.
4.8 Construction in accordance with current legislation is carried out under the control of local governments and state construction supervision. To ensure this possibility, the above-mentioned bodies must be notified in advance by the developer (customer) about the timing of the start of work on the construction site, about the suspension, conservation and (or) termination of construction, about the readiness of the facility for commissioning.
4.9 Upon completion of the construction of a building or structure, an assessment is made of its compliance with the requirements of current legislation, technical regulations, design and working documentation, its acceptance during construction on the basis of a contract, as well as the commissioning of the completed building or structure.
4.10 Construction control carried out by construction participants must be carried out in accordance with the Federal Law of June 26, 2008 No. 102-FZ “On Ensuring the Uniformity of Measurements” using measuring instruments of an approved type that have been tested, according to certified methods (methods) where necessary. measurements. Routine tests and measurements must be carried out by qualified personnel.
5 Preparation for construction
5.1 In order to carry out construction on the basis of a contract, the developer (customer) engages a contractor (general contractor) to perform work in accordance with current legislation as the person carrying out the construction.
5.2 Construction participants (legal entities), with their administrative documents (orders), appoint officials personally responsible for construction:
developer (customer)- responsible representative of the construction control of the developer (customer);
person carrying out construction (contractor, general contractor),- responsible producer of the work;
the person who prepared the design documentation (designer),- the responsible representative of the designer's supervision in cases where the designer's supervision is carried out.
These officials must have qualifications that meet the requirements of current legislation.
When a building or structure is constructed by a legal entity performing the functions of a developer (customer) and a person carrying out construction (contractor), these officials are appointed by the head of this organization. At the same time, combining the functions of the responsible work producer and the responsible representative of the construction control of the developer (customer) by one division or official of this organization is unacceptable.
5.3 The person carrying out the construction, in accordance with the currentlegislationmust have certificates of admission to types of work that affect the safety of the building or structure being constructed, issued by a self-regulatory organization.
5.4 When carrying out construction on the basis of a contract, the developer (customer) transfers to the person carrying out the construction the design documentation approved by him, as well as working documentation for the entire facility or for certain stages of work in two copies on electronic and paper media. Design and working documentation must be approved for work by the developer (customer) with the signature of the responsible person by placing a stamp on each sheet. The composition and content of sections of project documentation (including the construction organization project) transferred to the person carrying out construction must comply with the requirements established by the Government of the Russian Federation (Appendix A). The transferred design documentation must contain the designer's assurance that this documentation has been developed in accordance with the design assignment and the requirements of the Federal Law of December 30, 2009 L "" 384-FZ "Technical Regulations on the Safety of Buildings and Structures".
5.5 The person carrying out the construction carries out incoming inspection of the working documentation transferred to him for execution, transmits to the developer (customer) a list of deficiencies identified in it, and verifies their elimination. The deadline for completing the incoming inspection of project documentation is established in the contract.
At the same time, the person carrying out the construction can check the possibility of implementing the project using known methods, determining, if necessary, the need for the development of new technological methods and equipment, as well as the possibility of acquiring materials, products and equipment, the use of which is provided for in the design documentation, and the compliance of the actual location specified in design documentation of the places and conditions for connecting temporary utility lines (networks) to external utility networks to provide the construction site with electricity, water, heat, and steam.
5.6 Conditions for fulfillment during construction; requirements of legislation on labor protection, the environment and the population, as well as the possibility of performing all types of control necessary to assess the compliance of the work performed with the requirements of design, regulatory documentation and (or) the terms of the contract, are established by construction organization projects and organizational and technological documentation.
5.7 Design preparation of construction organization and organizational and technological documentation
5.7.1 Solutions for organizing construction for industrial and non-industrial facilities are developed in projects for organizing construction and projects for organizing work on the demolition or dismantling of capital construction projects. Solutions for organizing construction for linear objects are developed in projects for organizing construction and projects for organizing work on the demolition (dismantling) of a linear object. Projects for the organization of construction, projects for the organization of work for the demolition or dismantling of capital construction projects, projects for the organization of work for the demolition (dismantling) of a linear facility (hereinafter referred to as construction organization projects, POS) are an integral and integral part of the project documentation. Construction organization projects are a mandatory document for the developer (customer), contractors, as well as organizations providing financing and logistics.
The choice of decisions on the organization of construction should be carried out on the basis of variant study with the widespread use of criteria-based assessment methods, modeling methods and modern computer systems.
5.7.2 Organizational and technological documentation includes a project for the production of work, as well as other documents that contain decisions on the organization of construction production and technology for construction and installation work, drawn up, agreed upon, approved and registered in accordance with the rules in force in organizations developing, approving and coordinating these documents.
5.7.3 The work project (hereinafter referred to as the WPR), as well as other documents containing decisions on the organization of construction production and the technology of construction and installation work, are approved by the person performing the construction.
5.7.4 The work project must be developed in full:
- during any construction in urban areas;
- during any construction on the territory of an existing enterprise;
- during construction in difficult natural and geological conditions, as well as technically particularly complex objects - at the request of the authority issuing a construction permit or for construction, installation and special work.
In other cases, the PPR is developed by decision of the person carrying out construction in an incomplete volume.
5.7.5 The full scope of work project includes:
- calendar plan for the production of work on the facility;
- construction master plan:
- schedule for the arrival of building structures, products, materials and equipment at the site;
- schedule of movement of workers around the facility;
- movement schedule of the main construction vehicles around the site;
- technological maps for performing types of work;
- layout of geodetic signs:
- an explanatory note containing decisions on geodetic work, decisions on laying temporary networks of water, heat, energy supply and lighting of the construction site and workplaces; justifications and measures for the use of mobile forms of work organization, work and rest schedules: decisions on the production of work, including winter time: the need for energy resources; the need and connection of construction camps and mobile (inventory) buildings; measures to ensure the safety of materials, products, structures and equipment at the construction site: environmental protection measures; occupational health and safety measures in construction; technical and economic indicators.
The part-time work project includes:
- construction master plan;
- technological maps for performing certain types of work (as agreed with the customer):
- layout of geodetic signs;
- an explanatory note containing the main decisions and environmental measures; measures for labor protection and safety in construction.
5.7.6 The starting materials for developing work projects are:
- a development assignment issued by a construction organization as the customer of the work project, with justification for the need to develop it for the building (structure) as a whole, its part or type of work and indicating the development time frame;
- construction organization project;
- necessary working documentation;
- conditions for the supply of structures, finished products, materials and equipment, the use of construction machines and vehicles, the provision of workers for builders in the main professions, the use of team contracts for the execution of work, production and technological equipment and transportation of construction goods, and, in necessary cases, also the conditions for organizing construction and performing work on a rotational basis; - materials and results of technical inspection of existing enterprises, buildings and structures during their reconstruction, as well as requirements for the performance of construction, installation and special construction work in the conditions of existing production.
5.7.7 Solutions for work projects must ensure the achievement of safety of capital construction projects.
In the work project, deviations from the decisions of the construction organization project are not allowed without agreement with the organizations that developed and approved it.
5.7.8 If a PPR for the construction of a given facility is not developed, safety decisions are drawn up in the form of a separate document(s).
5.7.9 The project for carrying out work on the territory of an existing enterprise must be agreed upon with the organization operating it.
5.7.10 The project for carrying out work involving mining, blasting and other potentially hazardous work must also be agreed upon with the Rostechnadzor body.
5.8 The developer (customer) must ensure that the geodetic alignment base is brought to the site by a person who has a certificate of admission issued by a self-regulatory organization to work on creating geodetic support networks.
5.9 The person carrying out construction should check whether the organizational and technological documentation used by him contains instructions on carrying out construction control.
5.10 The person carrying out the construction should, on the basis of the design documentation, prepare diagrams of the location of the axes of buildings and structures to be laid out in nature, signs for securing these axes and installation landmarks, as well as diagrams of the location of structures and their elements relative to these axes and landmarks. The diagrams are developed based on the condition that the axes and landmarks laid out in kind must be technologically accessible for observation while monitoring the accuracy of the position of structural elements at all stages of construction.
At the same time, if necessary, it is necessary to adjust the existing one or develop a methodology for performing and monitoring the accuracy of geodetic alignment work, rules for applying and securing installation landmarks.
5.11 The person carrying out the construction, if necessary, should train personnel, as well as enter into agreements with accredited laboratories to perform those types of tests that the contractor cannot perform on his own.
5.12 In preparation for construction and installation work on the territory of existing production facilities, the administration of the developer and the person carrying out the construction appoint a person responsible for the operational management of the work and determine the procedure for coordinated actions. At the same time, the following is determined and agreed upon:
- volumes, technological sequence, timing of construction and installation work, as well as conditions for combining them with the work of production shops and sections of the enterprise being reconstructed;
- the procedure for operational management, including the actions of builders and operators, in the event of emergency situations;
- the sequence of dismantling structures, as well as dismantling or relocating utility networks, places and conditions for connecting temporary water supply networks, electricity supplies, etc., locations for as-built surveys;
- the procedure for builders to use the services of the enterprise and its technical means;
- conditions for organizing the complete and priority supply of equipment and materials, transportation, storage of goods and movement of construction equipment throughout the enterprise, as well as the placement of temporary buildings and structures and (or) use for the needs of the construction of buildings, structures and premises of an existing production enterprise.
5.13 Measures to close streets, restrict traffic, change the movement of public transport, provided for by the construction plan and agreed upon during its development, are finally agreed upon by the developer (customer) with the State Road Safety Inspectorate of the internal affairs bodies and transport and communications institutions of the local government before the start of work. Once the need for restrictions ceases, these authorities must be notified.
6 Construction work
6.1 Construction work must be carried out by the person carrying out the construction in accordance with current legislation, design, working and organizational and technological documentation.
6.2 Construction site
6.2.1 The boundaries of the construction site must be indicated on the construction plan and the situational plan, and for linear objects - indicated in the form of the width of the right of way.
6.2.2 In addition to the land plot owned by the developer, the construction site may, if necessary, additionally include the territories of other (including neighboring) land plots. In such cases, the developer, before obtaining a construction permit, must obtain the consent of the owners of additional territories for their use, or the necessary easements must be established.
6.2.3 Security of the construction site, compliance with labor protection requirements at the construction site, environmental protection, safety of construction work for the surrounding area and population, as well as compliance with various administrative requirements established by these standards, other current regulatory documents or local government bodies, is ensured by the developer .
6.2.4 If construction is carried out on the basis of a contract, during the entire construction period the stipulated years. 6.2.3 responsibilities in accordance with the contract are performed by the contractor (general contractor).
6.2.5 If construction is carried out on the basis of a contract, the developer (customer) transfers the construction site to the contractor (general contractor) as the person carrying out the construction, according to the act. The area and condition of the construction site must comply with the terms of the contract. The developer (customer) in accordance with the currentlegislationin the cases and in the manner provided for by the contract, must transfer for use to the contractor (general contractor) the buildings and structures necessary for the implementation of the work, ensure the transportation of goods to his address, temporary installation of power supply networks, water and steam pipelines.
6.2.6 The person carrying out the construction must [ensure cleaning of the construction site and the five-meter adjacent area. Household and construction waste, as well as snow, must be removed in a timely manner and in the manner established by the local government.
6.2.7 If necessary, at the request of a local government body, the person carrying out the construction must equip the construction site facing the urban area with cleaning or washing points for vehicle wheels at exits, as well as devices or bins for collecting waste, and on linear objects - in the places indicated local government body.
If it is necessary to temporarily use certain territories not included in the construction site for construction needs that do not pose a danger to the population and the environment, the regime of use, protection (if necessary) and cleaning of these territories is determined by agreement with the owners of these territories (for public territories - with local government body).
6.2.8 The person carrying out construction, before starting any work, must fence off the construction site and hazardous work areas outside it in accordance with the requirements of regulatory documents.
At the entrance to the site, information boards with instructions should be installed. name of the object, name of the developer (customer), performer of the work (contractor, general contractor), surname, position and telephone numbers of the responsible producer of work on the object and a representative of the state construction supervision body (in cases where supervision is carried out) or local government supervising construction, start and end dates works, facility diagrams.
The name and telephone number of the work performer are also placed on the inventory fencing panels of off-site work sites, mobile buildings and structures, large equipment elements, cable drums, etc.
6.2.9 If the operation of existing and abandoned buildings and structures on a construction site is terminated, the developer must take measures to prevent harm to the population and the environment (communications are disconnected, existing containers are emptied, hazardous or toxic substances are removed, etc.). The person carrying out the construction must take measures to prevent unauthorized access to the building by people and animals.
6.2.10 On-site preparatory work must be completed before the start of construction and installation work in accordance with the work project.
6.2.11 During the entire construction period, the person carrying out the construction must provide access to the construction site and the building (structure) under construction to representatives of the construction control of the developer (customer), architectural supervision and state supervisory authorities.
6.3 In cases where construction is carried out in an area exposed to adverse natural phenomena and geological processes (mudflows, avalanches, landslides, landslides, swamps, flooding, etc.), prior to the start of construction work on special projects, carry out priority activities and work on protecting the territory from these processes.
6.4 Incidental development of natural resources can be carried out in the presence of appropriate documentation agreed upon and approved in accordance with the established procedure.
6.5 If objects of historical, cultural or other value are discovered during the work, the person carrying out the construction shall suspend the ongoing work and notify the institutions and bodies provided for by law about the discovered objects.
6.6 Temporary buildings and structures
6.6.1 Temporary buildings and structures for construction needs are erected (installed) on a construction site or in the right of way of linear objects by the person carrying out the construction, specifically to ensure construction and are subject to liquidation after its completion. Temporary buildings and structures should mainly be inventory.
Buildings, structures or premises used for construction purposes that are part of the construction project are not considered temporary.
6.6.2 If it is necessary to temporarily use certain territories not included in the construction site for the placement of temporary buildings and structures, the regime of use, protection (if necessary) and cleaning of these territories is determined by an agreement with the owners of these territories (for public territories - with the local government).
6.6.3 Temporary buildings and structures, as well as separate premises in existing buildings and structures, adapted for use for construction needs, must comply with the requirements of technical regulations and current construction, fire, sanitary and epidemiological norms and rules for domestic, industrial, administrative and residential buildings , structures and premises.
6.6.4 Temporary buildings and structures located on a construction site or on territory used by the developer by agreement with its owner are put into operation by decision of the person carrying out the construction. Commissioning is formalized by an act or an entry in the work log.
6.6.5 Responsibility for the safety of temporary buildings and structures, as well as individual premises in existing buildings and structures adapted for use for construction needs, for their technical operation lies with the person carrying out the construction.
6.7 Temporary settlements created for the needs of construction of the facility are located on the territory of the developer or on the territory used by the developer by agreement with its owner. The temporary settlement project must include a master plan tied to the area, the composition of temporary buildings, structures and (or) premises, electrical, water, heat supply and sewerage diagrams, a diagram of access roads for all types of transport used, and communication solutions. The temporary settlement project should also include its demolition, land reclamation, and cost estimates for these works.
6.8 In cases where the developer provides for the subsequent transfer of temporary settlements, buildings and structures for permanent operation, projects for temporary settlements, buildings and structures are developed, agreed upon and approved in the manner established for the design of settlements, buildings and structures intended for permanent use for their intended purpose. The commissioning of such settlements, buildings and structures into permanent operation is carried out in the manner established by the legislation on urban planning activities.
6.9 Liquidation and demolition of buildings and structures
6.9.1 Work on the liquidation and demolition of buildings and structures must be carried out in accordance with the project for organizing the demolition or dismantling work, which includes a list of buildings and structures to be demolished, as well as the necessary technical solutions for demolition, ensuring the safety of builders, the population, the environment and engineering infrastructure, including existing underground communications.
6.9.2 Liquidated buildings and structures from the moment of their decommissioning until the moment of their liquidation (demolition) must be brought into a safe condition, excluding accidental harm to the population and the environment (communications must be turned off, existing containers emptied, hazardous or toxic substances removed, secured or unstable structures collapsed, etc.). Measures must be taken to prevent unauthorized access of people and animals to these buildings (structures).
6.9.3 Everyone on the construction site, as well as the organization operating the adjacent territory, must be notified of the moment of explosion, burning or collapse of a demolished building or structure. If necessary, a cordon should be set up.
6.9.4 The relevant accounting and administrative authorities must be notified of the fact of liquidation or demolition of a building or structure. At the same time, the bodies holding territorial geofunds, in the order established by them, must be informed about the communications, premises, structures and structures remaining in the ground.
6.10 Warehousing and storage of materials, products and structures used (purchased and manufactured in-house) in accordance with the requirements of standards and technical specifications for these materials, products and structures is provided by the person carrying out the construction.
If violations of the established warehousing and storage rules are detected, the person carrying out the construction must immediately eliminate them. The use of improperly stored and stored materials and products by the person carrying out the construction must be suspended until the issue of the possibility of their use without compromising the quality of construction by the developer (customer) is resolved, with the involvement, if necessary, of representatives of the designer and the state construction supervision body. This decision must be documented.
6.11 When carrying out work related to the construction of temporary excavations and other obstacles on the territory of an existing building, the person carrying out the construction ensures the passage of vehicles and access to houses by constructing bridges, pedestrian bridges with handrails, and ladders in agreement with the owner of the territory. After completion of the work, the specified devices must be removed from the territory, and the landscaping of the territory must be restored.
Work areas must be fenced to prevent unauthorized entry of people and animals.
Work areas, as well as temporary passages and passages must be illuminated.
Organizational and technological solutions should be focused on maximizing the reduction of inconvenience caused by construction work to the population. For this purpose, the laying of communications in urban areas along streets and roads must be carried out according to a schedule that takes into account their simultaneous installation; restoration of landscaping should be carried out in areas usually no more than one block long; restoration work should be carried out in two or three shifts; asphalt concrete waste and construction waste should be removed in a timely manner and in the manner established by the local government.
6.12 Work in the locations of existing underground utilities
6.12.1 Work related to opening the surface at the locations of existing underground communications and structures must be carried out in compliance with special rules established by the ministries and departments operating these communications, as well as the following additional rules.
6.12.2 In accordance with the current rules for the protection of underground communications, the responsible work contractor must, no later than three working days, call to the work site representatives of organizations operating existing underground communications and structures, and in their absence, representatives of organizations that approved the design documentation.
If there are no communications and structures operated by them in the specified place of work, the relevant organizations are obliged to officially notify the person carrying out the construction about this.
6.12.3 Representatives of operating organizations arriving at the site are presented with design and working documentation and actual axles or dimensions of the intended excavation. Together with the operating organization, the actual position of existing underground communications and structures is determined on site (by excavation or other means), marked on the ground and plotted on working drawings. Representatives of operating organizations provide the person carrying out the construction with instructions on measures to ensure the safety of existing underground communications and structures and on the need to call them to inspect hidden work and at the time of backfilling excavations.
Organizations that did not appear and did not notify about the absence of communications and structures operated by them at the work site are called again one day before, with simultaneous notification of local authorities, who decide on further actions in the event of repeated failure of representatives of these organizations to appear. Work cannot begin until the appropriate decision is made.
The responsible operator of the work is obliged to instruct the operator of the earthmoving machine on the procedure for developing the excavation and to mark with clearly visible signs from the cab the boundaries of the zone within which mechanized excavation of the pound is allowed. The remaining soil mass, immediately adjacent to the underground structure, is excavated manually.
6.13 The person carrying out construction, in accordance with the legislation on urban planning activities, must maintain executive documentation:
- certificates of inspection of the geodetic alignment basis of a capital construction project;
- acts of laying out the axes of a capital construction object
on the ground;
- certificates of inspection of hidden work;
- certificates of inspection of critical structures;
- certificates of inspection of sections of engineering support networks;
- a set of working drawings with inscriptions on the compliance of the work performed in kind with these drawings or on the changes made to them in agreement with the designer by the persons responsible for the construction and installation work;
- executive geodetic diagrams and drawings;
- executive diagrams and profiles of sections of engineering support networks;
- certificates of testing and testing of technical devices:
- results of examinations, surveys, laboratory and other tests of completed work carried out during the process of construction control;
- documents confirming quality control of the building materials (products) used;
- other documents reflecting the actual implementation of design decisions.
Requirements for the preparation and procedure for maintaining executive documentation are established by the Federal Service for Environmental, Technological and Nuclear Supervision.
6.14 As work and structures are ready, the quality indicators of which affect the safety of the building (structure), and if, in accordance with the construction technology, these indicators cannot be controlled after subsequent work, the person carrying out the construction, within the agreed time frame, but no later than notifies the developer (customer), representatives of state control (supervision) and architectural supervision authorities three working days in advance about the timing of the relevant conformity assessment procedure.
The shortcomings identified by such a procedure must be eliminated with the drawing up of appropriate acts.
Until the identified deficiencies are eliminated and the relevant acts are completed, subsequent work is unacceptable.
6.15 Termination of construction and conservation of the facility
6.15.1 If it is necessary to stop construction work or suspend it for a period of more than 6 months. conservation of the object must be carried out - bringing the object and the territory used for construction to a state that ensures the strength, stability and safety of the main structures and the safety of the object for the population and the environment.
6.15.2 The decision to terminate or suspend construction is made by the developer and notifies the person carrying out the construction (if construction is carried out on the basis of a contract), the local government body, as well as the relevant state supervisory authorities about the decision. Responsibility for the safety of a facility whose construction is terminated or suspended lies with the developer.
6.15.3 The fact of termination or suspension of construction within three days must be notified, if necessary, to the traffic police of internal affairs bodies in order to cancel previously introduced restrictions on the movement of vehicles and pedestrians, as well as the owners of territories included in the territory of the construction site in accordance with the approved and agreed construction plan.
When carrying out construction on the basis of a contract, the developer (customer) and the person carrying out the construction when carrying out construction on the basis of a contract, no later than a month later draw up an act of acceptance of the completed part of the object with a description of the condition of the object, indicating the volume and cost of work performed, a statement of applied (installed) ) at the site of equipment, materials and structures, a list of unused equipment, materials and structures subject to storage, a list of works necessary for the safety of the facility and unused equipment, materials and structures.
6.15.4 If necessary, the designer, under an agreement with the developer (customer), develops working drawings and an estimate for the conservation of the object, and the person carrying out the construction carries out the work provided for by these working drawings and estimates.
6.15.5 When construction is carried out on the basis of a contract, the mothballed object and the construction site are transferred according to an act to the developer (customer). The act is accompanied by as-built documentation, work logs, as well as documents on surveys, inspections, control tests, measurements carried out during construction, documents from suppliers confirming the compliance of materials, work, structures, technological equipment and engineering systems of the facility with the project and the requirements of regulatory documents.
7 Construction quality control. Supervision of construction
7.1 Construction participants - the person carrying out the construction, the developer (customer), the designer - must carry out construction control provided for by the legislation of the Russian Federation on urban planning activities in order to assess the compliance of construction and installation works, erected structures and engineering support systems for a building or structure with the requirements technical regulations, design and working documentation.
The person carrying out construction, as part of construction control, performs:
- incoming control of design documentation provided by the developer (customer);
- survey of the geodetic alignment basis of a capital construction project;
- incoming inspection of used building materials, products, structures and equipment;
- operational control during the execution and upon completion of construction and installation operations;
- examination of completed work, the results of which become unavailable for control after the start of subsequent work;
- inspection of critical building structures and sections of engineering support systems;
Testing and testing of technical devices. Construction control of the developer (customer) in accordance with current legislation is carried out in the form of control and supervision of the customer over the performance of work under the construction contract in accordance with 7.3.
In the cases provided for in 7.4, as part of construction control, designer supervision is carried out by the person who prepared the design documentation (designer).
7.1.1 During the incoming inspection of project documentation, you should analyze all submitted documentation, including PIC and working documentation, checking:
- its completeness;
- compliance of the design axial dimensions and the geodetic basis;
- availability of agreements and approvals;
- availability of links to regulatory documents on materials and products;
- compliance of the construction site boundaries on the construction plan with the established easements;
- existence of requirements for the actual accuracy of controlled parameters;
- availability of instructions on control and measurement methods, including in the form of links to relevant regulatory documents.
If deficiencies are found, the relevant documentation is returned for revision within the period specified in the contract.
7.1.2 The person carrying out the construction accepts the geodetic alignment base provided to him by the developer (customer), checks its compliance with the established requirements for accuracy, and the reliability of fixing the signs on the ground; for this purpose, it is possible to attract independent experts who have a certificate of admission to work on the creation of geodetic support networks issued by a self-regulatory organization.
Acceptance of the geodetic alignment base from the developer (customer) should be formalized by the appropriate act.
7.1.3 Incoming control checks the compliance of the quality indicators of purchased (received) materials, products and equipment with the requirements of standards, technical specifications or technical certificates for them specified in the project documentation and (or) the contract.
At the same time, the presence and content of accompanying documents of the supplier (manufacturer) are checked, confirming the quality of the specified materials, products and equipment.
If necessary, control measurements and tests of the above indicators can be performed. The methods and means of these measurements and tests must comply with the requirements of national standards. The results of the incoming inspection must be documented in the incoming inspection and (or) laboratory test logs.
7.1.4 If control and testing is carried out by contracted laboratories, the compliance of the control and test methods they use with the established national standards should be verified.
7.1.5 Materials, products, equipment, the non-compliance with established requirements was revealed by incoming inspection, should be separated from suitable ones and marked. Work using these materials, products and equipment should be suspended. The developer (customer) must be notified of the suspension of work and its reasons.
In accordance with the law, one of three decisions can be made:
- the supplier replaces non-conforming materials, products, equipment with appropriate ones;
- non-conforming products are reworked;
- non-conforming materials and products can be used after mandatory agreement with the developer (customer), designer and state control (supervision) body within its competence.
7.1.6 With operational control, the person carrying out the construction checks:
- compliance of the sequence and composition of the technological operations performed with the technological and regulatory documentation applicable to these technological operations;
- compliance with technological regimes established by technological maps and regulations;
- compliance of quality indicators of operations and their results with the requirements of design and technological documentation, as well as regulatory documentation applicable to these technological operations.
The places where control operations are performed, their frequency, performers, methods and measuring instruments, forms for recording results, the procedure for making decisions when identifying non-conformities with established requirements must comply with the requirements of design, technological and regulatory documentation.
The results of operational controls should be documented in work logs.
7.2 During the construction process, an assessment must be made of completed work, the results of which affect the safety of the facility, but in accordance with the adopted technology become unavailable for control after the start of subsequent work, as well as completed building structures and sections of utility networks, the elimination of defects identified by control impossible without dismantling or damaging subsequent structures and sections of utility networks. Representatives of the relevant state supervision bodies, designer’s supervision, as well as, if necessary, independent experts may participate in these control procedures. The person carrying out the construction, within the terms agreed upon, but no later than three working days, notifies the other participants about the timing of the specified procedures.
7.2.1 The results of the inspection of work hidden by subsequent work, in accordance with the requirements of design and regulatory documentation, are documented in acts of inspection of hidden work. The developer (customer) may require a re-inspection after eliminating the identified defects.
7.2.2 To the procedure for assessing the conformity of individual structures, tiers of structures (floors), the person carrying out the construction must submit inspection reports of all hidden works included in these structures, geodetic as-built diagrams, as well as test reports of structures in cases provided for by the design documentation and (or) construction contract. The developer (customer) can check the accuracy of the as-built geodetic schemes presented by the contractor. For this purpose, the person carrying out the construction must preserve the alignment axes and installation guidelines fixed in kind until the completion of acceptance.
The results of the inspection of individual structures must be documented in inspection reports of critical structures.
7.2.3 Tests of sections of utility networks and installed utility equipment are carried out in accordance with the requirements of the relevant regulatory documents and are documented in the relevant acts.
7.2.4 If defects in work, structures, or sections of utility networks are discovered as a result of construction inspection, the corresponding acts must be drawn up only after the identified defects have been eliminated.
In cases where subsequent work must begin after a break of more than six months from the completion of phased acceptance, before resuming work, these procedures should be repeated with the execution of the relevant acts.
7.3 Construction control of the customer is carried out by:
- checking that the person carrying out the construction has quality documents (certificates in certain cases) for the materials, products and equipment he uses, documented results of incoming inspection and laboratory tests;
- control of compliance by the person carrying out the construction with the rules of warehousing and storage of used materials, Products and equipment; if violations of these rules are detected, a representative of the construction control of the developer (customer) may prohibit the use of improperly stocked and stored materials;
- monitoring compliance of the operational control carried out by the person carrying out the construction with the requirements of 7.1.6;
- control of the availability and correctness of as-built documentation by the person carrying out construction, including assessment of the reliability of geodetic as-built diagrams of completed structures with selective control of the accuracy of the position of elements;
- control over the elimination of defects in design documentation identified during the construction process, documented return of defective documentation to the designer, control and documented acceptance of corrected documentation, transfer of it to the person carrying out construction;
- control over the execution by the person carrying out the construction of instructions from state supervisory authorities and local self-government;
- notification of state supervisory authorities about all cases of emergency conditions at the construction site;
- assessment (together with the person carrying out the construction) of the conformity of the work performed, structures, sections of utility networks, signing of bilateral acts confirming compliance; control over the fulfillment by the person carrying out the construction of the requirement that subsequent work is inadmissible before the signing of the specified acts;
- final assessment (together with the person carrying out the construction) of the compliance of the completed facility with the requirements of legislation, design and regulatory documentation.
7.4 During the construction of hazardous production facilities, as well as particularly dangerous, technically complex and unique facilities, designer supervision is carried out. In other cases, it is carried out by the decision of the developer (customer). The procedure for implementation and functions of designer's supervision are established by relevant documents.
7.5 Comments from representatives of the construction control of the developer (customer) are documented in the general and special work logs, comments from representatives of the architectural supervision - in the architectural supervision log. The facts of elimination of defects based on the comments of these representatives are documented with their participation.
7.6 The author's supervision of the architect is carried out by the author-architect on his own initiative, regardless of the decision of the developer (customer) and the existence of an agreement for author's supervision of the object. The territorial body for architecture and urban planning, at the request of the author, having verified his authorship, may issue an order to the developer (customer) to ensure the author's access to the construction site and the possibility of him making entries in the author's supervision journal. Claims of the author-architect regarding the implementation of architectural design solutions may be considered by the body for urban planning and architecture, the decision of which is binding on the developer (customer).
7.7 State construction supervision is carried out in cases provided for by the legislation on urban planning activities in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation on urban planning activities and other regulatory legal acts (Appendix A).
State construction supervision authorities assess the conformity of the construction process of a specific facility upon receipt of a notification from the developer (customer) about the start of construction work.
7.8 In order to limit the adverse impact of construction and installation work on the population and territory in the zone of influence of ongoing construction, local government bodies or organizations authorized by them (administrative inspections, etc.) carry out administrative control over construction in the manner established by current legislation.
Administrative control consists of preliminary establishment of construction conditions (dimensions of construction site fencing, temporary work schedule, waste removal, maintaining order in the adjacent territory, etc.) and monitoring compliance with these conditions during construction. The developer is responsible to the local government, unless otherwise provided by the agreements.
The conditions for construction are established in the form of a warrant or other document issued by the local administration or organizations authorized by it in accordance with the regulatory legal acts of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation.
Appendix A
(informative)
Regulations
Town Planning CodeRussian Federation
Civil CodeRussian Federation
the federal lawdated December 30, 2009 No. 384-FZ “Technical regulations on the safety of buildings and structures”the federal lawdated June 26, 2008 No. 102-FZ “On ensuring the uniformity of measurements”
ResolutionGovernment of the Russian Federation dated February 16, 2008 No. 87 “Regulations on the composition of sections of project documentation and requirements for their content”
the federal lawdated July 21, 1997 No. 116-FZ “On industrial safety of hazardous production facilities”
ResolutionGovernment of the Russian Federation dated February 1, 2006 No. 54 “Regulations on the implementation of construction supervision in the Russian Federation”
ResolutionGovernment of the Russian Federation dated November 24, 2005 No. 698 “On the form of a construction permit and the form of permission to put a facility into operation”
Bibliography
RD 11-02-2006Requirements for the procedure for maintaining as-built documentation during construction, reconstruction, major repairs of capital construction projects and requirements for certificates of inspection of construction work, sections of engineering support networks
RD 11-05-2007The procedure for maintaining a general and (or) special log of work performed during construction, reconstruction, major repairs of capital construction projects
SP 11-110-99Author's supervision of the construction of buildings and structures
RD 11-04-2006.The procedure for conducting inspections during state construction supervision and issuing conclusions on the compliance of constructed, reconstructed, repaired capital construction projects with the requirements of technical regulations (norms and rules), other regulatory legal acts and project documentation.
The main legislative acts are:
SNiP 12-03-2001 “Labor safety in construction. Part 1. General requirements" (approved on September 1, 2001 by Resolution of the State Construction Committee of Russia dated July 23, 2001 No. 80);
SNiP 12-04-2002 “Labor safety in construction. Part 2. Construction production" (approved by Resolution of the State Construction Committee of Russia dated September 17, 2002 No. 123).
This collection contains all the safety requirements for the work of construction organizations.
Status for 2019
For many years, the fundamental documents in this area were SNiP 12-03-2001 and SNiP 12-04-2002. What is their current status and are they still active in 2019? Let's answer the question.
On June 1, 2015, Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 26, 2014 No. 1521 came into force. It canceled the previously effective Decree No. 1047-r. From that moment on, SNiPs ceased to be considered mandatory documents for the employer.
Soon after this event, 08/28/2015 came into force. In 2019 they continue to be relevant. They operate for any construction work related to buildings and structures:
- construction of a new facility;
- Maintenance;
- carrying out major repairs;
- re-equipment;
- extension;
- modernization.
The rules are mandatory for use by both legal entities - construction organizations and individual entrepreneurs. In this connection, SNiPs are now used as recommendations, and legal priority is given to the Rules.
In 2019:
- SNiP occupational safety in construction, part 1, status - valid;
- SNiP occupational safety in construction, part 2, status - current.
Where to use
The current SNiP labor safety in construction establishes safety standards in construction, as well as in the production of building materials.
Previously, this document also regulated the relationship between the customer, contractor, general contractor, subcontractor, etc. and established responsibility for the performance of work. Now POTs play a leading role in this.
SNiP labor safety in construction, part 1
What regulates
Part 1 of SNiP occupational safety in construction (updated edition in 2010) contains general provisions for the application of regulatory legal acts that are mandatory in the construction industry.
It is worth noting that many documents that were mandatory at the time of approval of the first part are now not so. For example, these are Safety Standards, GOSTs, OSH rules. Currently, employers must follow the requirements of documents registered with the Ministry of Justice of the Russian Federation. And GOST and STB are applied on a voluntary basis.
Labor safety rules have also undergone changes since then. For example, the term “sweetjacking” is not currently used. Now this is “working at height.” The norms for carrying heavy objects manually, etc. have changed.
What does it contain requirements for?
The “General Safety Requirements” section of SNiP contains the following requirements:
- to the arrangement and maintenance of construction sites, production areas and workplaces;
- to storage of materials;
- to ensure electrical and fire safety;
- to the operation of lifting mechanisms, tools and devices.
In recent years, legislation in these areas has changed significantly. In this regard, when operating lifting mechanisms, it is necessary to be guided by Federal norms and rules in the field of industrial safety, as well as occupational safety rules when working with tools and devices, rules for loading and unloading operations and placement of cargo, labor protection during electric and gas welding work and gas cutting, with new rules on occupational safety in electrical installations, etc.
SNiP occupational safety in construction, part 2
General provisions
SNiP 12 04 “Labor safety in construction” is devoted to the organization of construction production, in particular, ensuring safety on the part of the general contractor. Clause 3.3 lists all the requirements for construction sites:
- the requirements for fencing the construction site are specified;
- clearing the territory for the construction of the facility;
- the construction of temporary roads, the laying of temporary power supply networks, lighting, and water supply are being considered;
- rules for placing domestic, industrial and administrative buildings and structures on the construction site, etc.;
- arrangement of crane tracks, storage areas for building materials and structures.
The end of the preparatory actions, according to clause 3.3, should be accepted according to the act on the implementation of occupational safety measures, drawn up in accordance with SNiP.
Work at the site must be carried out in technological sequence in accordance with the schedule contained in the PIC. Completion of previous work is an important condition for preparing and completing the following.
SNiP 12-04-2002 specifies the requirements for the composition of the PIC and PPR. The general contractor is responsible for the safety and health of the subcontractors and persons engaged in “individual labor activity” that he engages in work. Now this term is also inapplicable. Currently, the terms “individual entrepreneurs” and “individuals working under GPC agreements” are used.
Types of jobs
The section “Types of work” provides safety measures for the main types of construction work:
- earthen;
- drilling;
- installation;
- stone;
- finishing;
- insulating;
- roofing, etc.
In fact, each section contains ready-made material for instructions on occupational safety for construction workers.
The document specifies the rules that must be followed when carrying out high-risk work, for which a work permit must be drawn up, carried out under the approved construction organization plan and in stages - in each PPR. Just like Part 1, SNiP 12-04-2002 has the status of a document of voluntary application; its norms are not mandatory.
Express your opinion about the article or ask the experts a question to get an answer
In accordance with the requirements of paragraph 2 of the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated December 27, 2010 No. 1160 “On approval of the Regulations on the development, approval and amendment of regulatory legal acts containing state regulatory requirements for labor protection” (hereinafter referred to as Resolution No. 1160) to regulatory legal acts containing State regulatory requirements for labor protection include:
occupational safety standards;
rules and standard instructions on labor protection;
state sanitary and epidemiological rules and regulations (sanitary rules and regulations, sanitary standards, sanitary rules and hygienic standards that establish requirements for factors in the working environment and the labor process).
Thus, taking into account the requirements of Resolution No. 1160, it is obvious that the construction norms and rules SNiP 12-03-2001 “Labor safety in construction. Part 1. General requirements", approved. Resolution of the State Construction Committee of Russia dated July 23, 2001 No. 80 (hereinafter referred to as SNiP 12-03-2001) and SNiP 12-04-2002 “Labor safety in construction. Part 2. Construction production", approved. Decree of the Gosstroy of Russia dated September 17, 2002 No. 123 (hereinafter referred to as SNiP 12-04-2002), which for more than 10 years regulated the basic requirements for labor protection in construction, since 2011 objectively could not be appropriate regulatory legal acts containing state regulations labor protection requirements.
At the same time, despite the noted circumstances, SNiP 12-03-2001, SNiP 12-04-2002, even after the adoption of Resolution No. 1160, continued to retain the status of legitimate regulatory legal acts in the field of labor safety, the requirements of which are mandatory for execution in the construction industry. This legal status was given to these regulatory legal acts by Order of the Government of the Russian Federation dated June 21, 2010 No. 1047-r (hereinafter referred to as Order No. 1047-r), which approved the list of national standards and codes of practice (parts of such standards and codes of practice), as a result of the application which on a mandatory basis ensure compliance with the requirements of the Federal Law of December 30, 2009 No. 384-FZ “Technical Regulations on the Safety of Buildings and Structures”. Both SNiP 12-03-2001 and SNiP 12-04-2002 were included in the specified list.
However, by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated December 26, 2014 No. 1521 (hereinafter referred to as Resolution No. 1521), an updated list of national standards and sets of rules (parts of such standards and sets of rules) was approved, as a result of which, on a mandatory basis, compliance with the requirements of the Federal Law “Technical Regulations” is ensured on the safety of buildings and structures”, in which SNiP 12-03-2001 and SNiP 12-04-2002 no longer appeared. At the same time, Order No. 1047-r was declared invalid.
Resolution No. 1521 came into force on July 1, 2015. Thus, from this date, the requirements of SNiP 12-03-2001 and SNiP 12-04-2002 lost their mandatory status and could be implemented exclusively on a voluntary basis.
The following fact also seems legally important. Both SNiP 12-03-2001 and SNiP 12-04-2002 were adopted before the implementation of the Federal Law of December 27, 2002 No. 184-FZ “On Technical Regulation” (hereinafter referred to as Law No. 184-FZ), which came into force from 06/30/2003, i.e., when approving and registering these documents, it was not formally required that their norms comply with the requirements of Law No. 184-FZ. As a result, SNiP 12-03-2001 and SNiP 12-04-2002 contained norms related to the scope of legal regulation of Law No. 184-FZ and, in this regard, contradicting its requirements.
It is obvious that it was the combination of these circumstances that became the reason for the adoption, in the prescribed manner, of a new regulatory legal act defining mandatory labor protection requirements in construction. The rules for labor protection in construction were approved by order of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated 01.06.2015 No. 336n and from August 28, 2015 they came into force throughout the Russian Federation.